The role of add-on devices and how they affect drug delivery with a pressurized metered dose inhaler.

The role of add-on devices and how they affect drug delivery with a pressurized metered dose inhaler.
Experts discuss factors affecting drug delivery to the lungs and key considerations when developing inhalation formulations.

Products enable testing in accordance with methods described in new USP monograph.

In this sponsored podcast, Adam Stuart, Senior Design Engineer at 3M Drug Delivery Systems, discusses the role of dose counters for metered dose inhalers and the technical challenges companies can face when adding this feature to their inhaler products.

Stada licenses 3M's transdermal technology for a fentanyl patch.

Intertek is now offering comprehensive services for the development of orally inhaled and intranasal drug products (OINDPs) for both small molecules and biologics.

Bend Research adds powder-filling technology.

In this episode, we?ll discuss how an aging global population and the need for continual innovation in the pharmaceutical industry factor into drug delivery systems that move beyond traditional pills and capsules into transdermal drug delivery.

3M Drug Delivery will manufacture transdermal patch for ProStrakan.

Mylan completes expansion of its transdermal patch facility in Vermont.

Adamis Pharmaceuticals agrees to license and potentially acquire 3M's Taper Dry Powder Inhaler technology.

Australian team develops method for making ultrafine particles for more efficient drug delivery.

The challenge of developing orally inhaled nasal drug products (OINDPs) is complicated by the interplay between drug-delivery devices and formulation.

Even in an industry in which all product development is complicated by the intricacies of human biology, orally inhaled products (OIP) stand out as singularly demanding.

Micronization can be performed with a jet mill or bead mill.

New systems that combine Raman spectroscopy with automated imaging support the efficient gathering of such data, including information concerning size and shape distributions for individual components within a formulation.

Orphan drugs achieved blockbuster status in 2011, generating over $50 billion, and have the potential to generate as much lifetime revenue as drugs used for more common health conditions, according to a report from Thomson Reuters’ IP & Science division.
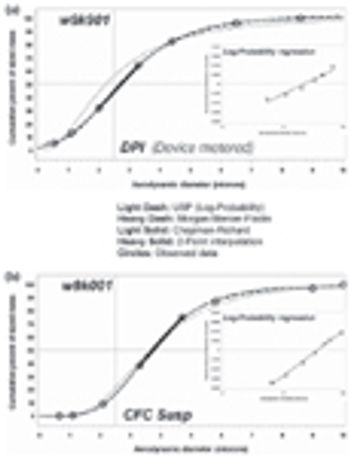
The authors discuss the analysis of the resulting data, focusing on methods for the calculation of mass median aerodynamic diameter, one of the metrics routinely used for comparative testing.

Emerging methods could provide alternative ways of producing inhalable drug particles.

The author reviews key considerations for formulating powders for use in inhalers. This article is part of a special Drug Delivery issue.
The author reviews advances in technology that may soon allow transdermal delivery of two of the fastest growing drug classes on the pharmaceutical market. This article is part of a special Drug Delivery issue.

Although there are no regulatory requirements or established pharmacopoeial techniques for the dissolution testing of inhaled drugs, such testing can potentially open up the opportunity to tailor formulation properties.

US Pharmacopeia apparatuses for testing the dissolution of transdermal drugs produce good, reproducible results. Yet some scientists believe that further modifications could improve the instruments? suitability for this application.

In a draft guidance published this week, the US Food and Drug Administration recommended that makers of transdermal and transmucosal drug-delivery systems use "an appropriate scientific approach" during product design, development, and manufacturing to minimize the amount of residual drug substance present at the end of the products' labeled use periods.

The pharmaceutical industry?s increasing interest in inhaled drugs has prompted several researchers to propose standard dissolution-testing methods for these products.