
As FDA implements new drug-safety policies, manufacturers will focus on quality and pricing.

As FDA implements new drug-safety policies, manufacturers will focus on quality and pricing.

Historically, the main purpose of laboratory information management systems (LIMS) has been to track and manage samples in the laboratory. LIMS originated nearly 30 years ago as a rudimentary method of automating manual, error-prone processes in the laboratory and, with the growth in adoption of technology, became the de facto benchmark for laboratory control and management.

Millipore and Novozymes Form Alliance, Applied Biosystems Names President and CEO, More

Merck & Co. initiated a voluntary recall of 11 lots of its Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine, Pedvaxhib, and two lots of its combination Haemophilus influenzae type B/ hepatitis B vaccine, Comvax.

Company and People Notes: West to reduce workforce, Eli Lilly's CEO and chairman to retire, more...

Company and People Notes: Eisai Acquires MGI Pharma, Ceregene Names CEO, More

Company and People Notes: Boehringer Ingelheim Expands Facility, Regulus Therapeutics Names President and CEO, More

Expansions
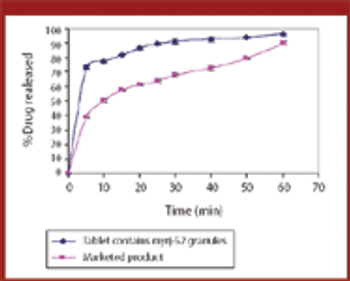
Various manufacturing techniques can improve a drug's solubility, thus increasing its bioavailability. The authors examined whether melt granulation can enhance drug solubility using meloxicam as the drug substance and myrj-52 as the binder.

In honor of Pharmaceutical Technology's 30th anniversary, the editors conducted a survey of 320 readers last spring to discuss industry advances and future directions. Here are some of your foward-looking responses.

Industry and regulatory organizations agree that the current focus on product quality will play a major role in shaping pharmaceutical development in the future. Key to this assessment of quality are the methods and technologies in pharmaceutical analytical testing.

How do you answer an inspector's questions? How do you validate analytical methods? One book has answers for compliance professionals.

"May you live in interesting times," goes the allegedly ancient Chinese curse. Well, these have been "interesting times" indeed for those working in the pharmaceutical industry.

Company and People Notes: ISP to raise prices, Patheon appoints CEO, more.

Company and People Notes: Cambridge Major Labs acquires ChemShop; Helix BioPharma restructures senior positions, more.

Company and People Notes: BASF raises prices on excipients; Verus Pharmaceuticals appoints president and CEO; more.

Submitting a safety update to European regulators, Novartis provided data showing its 100-mg once-daily dose of ?Galvus? (vidagliptin), an oral type 2 diabetes treatment, has more frequent liver enzyme elevations in patients than its already approved 50-mg once- and twice-daily doses.

Pfizer's Lipitor patent revoked in Germany, promotions at Charles River Labs, more.

Editors' Picks of Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Innovations

In this study, fault tree analysis applied to a water pretreatment and purification installation exposed cause-and-effect complex interrelations in possible fault events.

News and Views
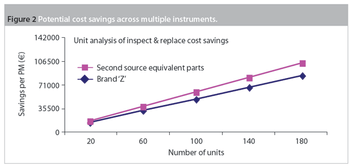
Maintenance and service-related items are often the second-largest budget element in a laboratory after salaries and benefits. Within maintenance, preventive maintenance (PM) is a substantial portion of the budget. Traditionally, PM was an equipment maintenance philosophy based on replacing, overhauling or remanufacturing a piece of equipment at fixed intervals, regardless of its condition at the time. In essence, it involved fixing something that wasn't necessarily broken and this approach is still widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.

Company Notes: Gibraltar expands facilities; Allozyne appoints new president and CEO, more.

Company and People Notes: ImClone, BMS, and Merck form agreement; CRI Worldwide names new CEO, more.

Company and People Notes: Orexo acquires Biolipox, Avalon cofounder resigns, more...