
Environmental monitoring, which operates below the limit of detection, is little more than a rote exercise that provides limited real value. So why does it figure so prominently in current regulatory requirements for aseptic manufacturing?
Russell E. Madsen is the former senior vice-president of science and technology at PDA, and is a current member of Pharmaceutical Technology's editorial advisory board.

Environmental monitoring, which operates below the limit of detection, is little more than a rote exercise that provides limited real value. So why does it figure so prominently in current regulatory requirements for aseptic manufacturing?

Validation ensures safe and effective biologic products that benefit the patients whose health and wellbeing depend on the therapies.

A previously published article presented difficulties with the revised European guidelines on sterile manufacturing. The authors included a brief summary of the comments developed on the draft document. This article expands upon that summary, outlines the authors' rationale, and highlights the most difficult aspects of the revision draft.

The revised Annex 1 on sterile manufacturing includes incorrect and ambiguous statements that must be fixed before implementation.

A book helps statistics novices prepare to comply with the US Food and Drug Administration's draft guidance on process validation.

How do you answer an inspector's questions? How do you validate analytical methods? One book has answers for compliance professionals.
Pre-use integrity testing of sterilizing-grade filters eliminates the potential adverse effects of filter loading on the integrity-test results, allowing unambiguous correlation with the integrity-test specification established during filter-validation studies.
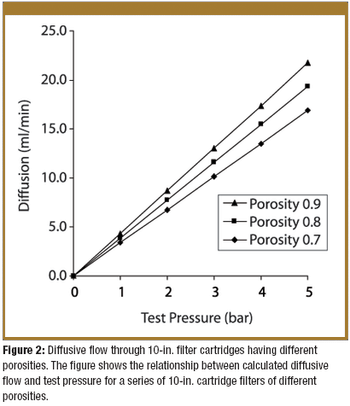
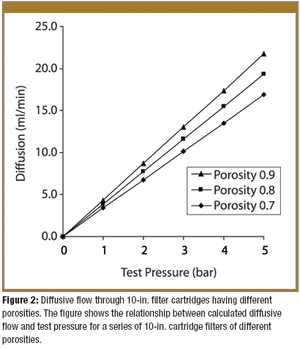
Pore-size ratings are so unrelated to actual dimensions and so subject to anomalous interpretations as to make substantial dependency upon their values an unwise choice. Moreover, the means of measuring them are questionable. The pore-size rating system at best provides a qualitative differentiation.

Model organisms are useful when validating sterile filtration, but successful retention of the model organism does not always guarantee that effluent is sterile. The authors explore the various factors that influence sterile filtration.

In spite of regulatory uncertainties, the industry continues to develop improved aseptic processing technologies.

In the concluding part of this article, the authors address diffusive-airflow imprecisions and measurements as well as automated integrity-test equipment, variations in bubble-point measurements, and the identification of a "sterilizing" filter.

In Part I of this article, the authors summarize the principles of various integrity tests, including their performance and purpose.

Published: November 2nd 2001 | Updated:

Published: October 2nd 2001 | Updated:

Published: May 2nd 2010 | Updated:

Published: December 2nd 2007 | Updated:
Published: May 1st 2007 | Updated:
Published: January 2nd 2007 | Updated: