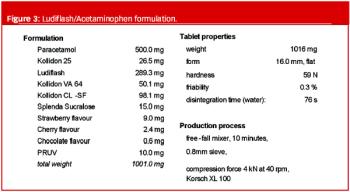
A new excipient for orally disintegrating tablets not only imparts superior tablet characteristics, but has the added advantage of allowing users to maintain full control over their formulations, manufacturing processes and intellectual property.

A new excipient for orally disintegrating tablets not only imparts superior tablet characteristics, but has the added advantage of allowing users to maintain full control over their formulations, manufacturing processes and intellectual property.

Hot-melt extrusion offers many advantages compared with conventional solid dosage form manufacturing, and has consequently received considerable attention from both the pharmaceutical industry and academia as a novel drug delivery technology. The possibility of forming solid dispersions with improved bioavailability renders hot-melt extrusion an excellent alternative to other conventionally employed techniques.

Also, Crucell and DSM announce deals with GSK, Talecris, and CSL; Nobel Prize winner Luc Montagnier joins Viral Genetics; more...

The US Food and Drug Administration issued a draft guidance, Genotoxic and Carcinogenic Impurities in Drug Substances and Products: Recommended Approaches.

Also, BASF opens lab in Mumbai; Evotek president and CEO to resign; more...

At its annual business briefing held last week, Merck & Co. outlined its short- and long-term strategy for growth. Its strategy is focused on increased penetration in emerging markets, the establishment of a business for developing follow-on biologics or biosimilars, and a new commercial model for product life-cycle management.

Also, NicOx and DSM make manufacture and supply pact for naproxcinod drug substance; NovaRx appointed Norrie Russell president and COO; more...

A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) study confirmed that severe adverse reactions reported in the fall and winter of 2007 resulted from heparin contaminated with oversulfated chondroitin sulfate (OSCS).

Also, AstraZeneca announces changes to its supply chain operations; Christian Velmer appointed head of Wyeth Canada; More...

The authors evaluated the effect of polymer composition on the drug-release profile and the effect of storage conditions on dissolution characteristics.

The past year saw major acquisitions attempted, completed, rejected, and stalled.

Readers provide insight into the best companies to work for as well as the ups and downs of their jobs.

China's quality approach to domestic versus exported products seems to be a lose-lose situation.
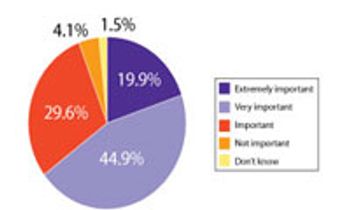
A recent Pharmaceutical Technology survey examined the level, sources, and reasons behind innovation in drug development and manufacturing. This article contains bonus online-exclusive material.

A book about pharmaceutical analysis engages the reader with history and unexpected asides.
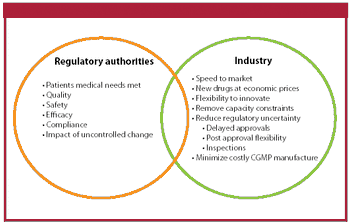
The authors review the current regulatory framework for the selection of drug substance starting materials.

Results from Pharmaceutical Technology's Annual Employment Survey.
Pharmaceutical Technology is pleased to recognize the winners of its Innovations in Pharma Science Awards.
How has pharmaceutical manufacturing validation influenced analytical instrument qualification during the last 20 years and what are the emerging trends for the future?

The closing date for comments to be received by the US Pharmacopeia (USP) for proposed revisions to Chapter <231>, which deals with analysis of heavy metals, is 15 December 2008. The USP has been working towards for approximately 4 years and the task has not been easy.
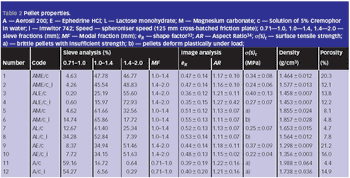
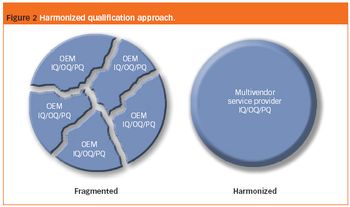
Microcrystalline cellulose is the main excipient used in the industrial manufacture of pellets by extrusion/spheronization, but pellets containing this spheronizing aid do not readily disintegrate and are expensive.
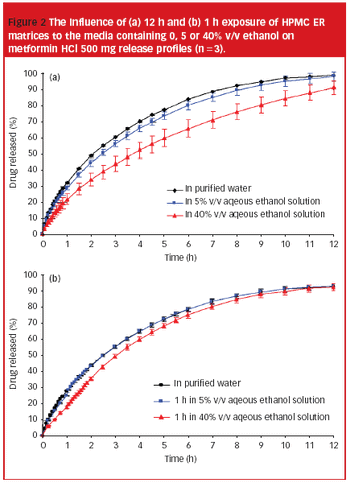
Research shows that both drug prescription and alcohol consumption increase within the elderly population. It is, therefore, necessary to fully understand the impact of alcohol consumption on solid oral dosage forms, especially extended release formulations.

Also, Johnson & Johnson will acquire Omrix Biopharmaceuticals for $438 million; Charles River Laboratories promoted Foster Jordan to corporate senior VP of endotoxin and microbial detection products; more...

Companies at the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scieintists (AAPS) unveiled technologies, expansion plans, and services for formulation development, manufacturing, and drug delivery at the AAPS Annual Meeting and Exposition held in Atlanta last week.

The American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS) recognized researchers in the pharmaceutical sciences at AAPS Annual Meeting and Exposition in Atlanta last week.