Securing the integrity of the excipient supply chain is a crucial task in ensuring the overall pharmaceutical supply chain. The authors outline excipient-control strategies and practices for the manufacture, distribution, and receipt of excipients.

Securing the integrity of the excipient supply chain is a crucial task in ensuring the overall pharmaceutical supply chain. The authors outline excipient-control strategies and practices for the manufacture, distribution, and receipt of excipients.

The design of accurate and robust analytical methodology is instrumental to developing orally inhaled and nasal drug products (OINDPs) and their appropriate control programmes.

The biggest benefit that has been brought about by the compulsory labelling of allergens in food is the greater degree of cooperation that has been established between food manufacturers and their suppliers.

Nanoparticles can also cross the blood–brain barrier, which could make them useful for delivering drugs that target brain tumours or diseases that affect the central nervous system.

The potent nature of HPAPIs means there must be careful evaluation of the compound for its level of toxicity when considering manufacture.
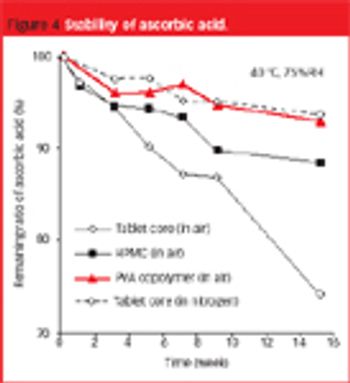
The use of PVA copolymer-based film can solve the problems associated with lack of film adhesion... to tablets containing large amounts of waxy excipient or a lubricant.

Also, Zentiva accepts Sanofi's increased takeover bid, Oriel Therapeutics appoints Richard Fuller CEO, more...

Also, Quintiles to expand Singapore operations; Christine A. Poon, chairman of Johnson & Johnson's pharmaceuticals group, to retire; more...

MannKind and Pfizer (New York) agreed that the former company will help patients who need inhaled insulin switch from Pfizer's "Exubera" medicine to MannKind's "Technosphere Insulin" drug.

Also, Human Genome Sciences enters pact with Hospira, Zosano Pharma names Gail Schulze chair and CEO, more...

Also, Novartis stops development on "Aurograb," Zealand Pharma appoints David H. Solomon as CEO, more...

Brief pharmaceutical news items for September 2008.

This year, the employment survey will acknowledge the industry's best employers.

With economics and politics in the way, can we defeat the malaria epidemic before it defeats us?
Carbon–hydrogen functionalization, ketone α-alkylation, and biocatalysis are some recent advances in asymmetric synthesis.

Are hypersanitation trends a result of scaremongering or a lack of faith in medicine?

The author explains the planning, equipment, and facility design requried for manufacturing HPAPIs and specialized requirements for handling these compounds.

The challenges of ineffective quality monitoring of complaints, investigations and adverse event reporting can lead to patient harm or death, product withdrawal, and negative financial and brand impact to the organization.

...some companies complained that what they received was not joint advice or combined advice but parallel advice, without coherence...

All commercial sponsors want to maximize their profit and, with a population close to 500 million, the EU is an enormous potential marketplace that they simply cannot ignore!
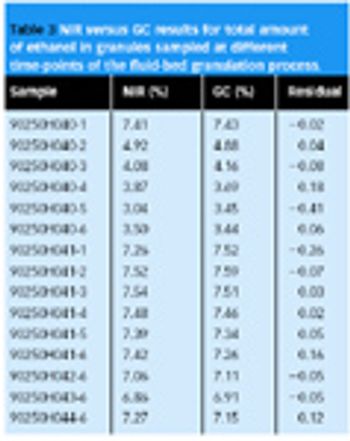
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR) is suitable for the analysis of pharmaceutical samples in various solid forms, and can be used for determining chemical properties (e.g., content of drug, water), as well as physical properties (e.g., particle size, tablet hardness).
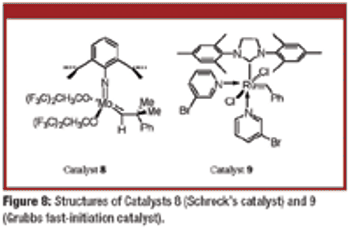
The authors describe the Piers' catalysts and detail latest progress in olefin-metathesis catalyst technology.
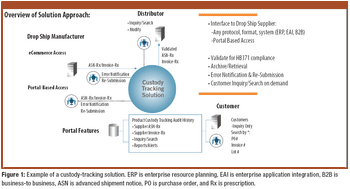
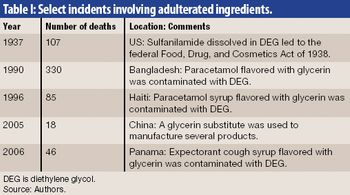
EPedigree, track-and-trace technologies, and other tools for optimizing supply-chain management are of increasing importance to the pharmaceutical industry. The author examines the current regulatory and legislative framework for ePedigree for finished drug products as well as proposals to require electronic statements for pharmaceutical ingredients.
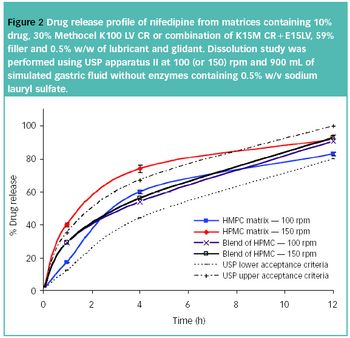
Different chemistries and viscosities of HPMC can be combined to modulate release profile and, in some cases, result in a more robust formulation.

The pharmaceutical industry is facing the perfect storm. Increasing healthcare costs, a changing regulatory environment and vigorous global competition coupled with the increasing complexity of small molecule and biotech drugs contributing to expensive discovery processes and clinical trials, as well as the resultant manufacturing challenges, all pose major threats to the industry.