
San Antonio, TX (Nov. 1)-Though the US Food and Drug Administration's final guidance on process analytical technology (PAT) was published in Sept. 2004, companies are still unsure about how exactly to implement PAT in their processes.

San Antonio, TX (Nov. 1)-Though the US Food and Drug Administration's final guidance on process analytical technology (PAT) was published in Sept. 2004, companies are still unsure about how exactly to implement PAT in their processes.
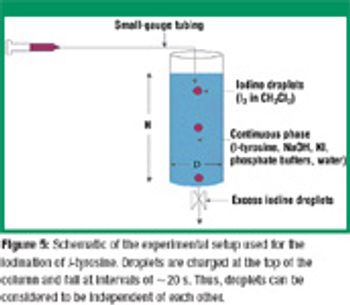
Understanding the impact of reactive mass transfer and local flow in multiphase systems is crucial for maximizing reaction selectivity and minimizing the formation of byproducts. The authors study the influence of mixing on fast liquid–liquid reactions. The iodination of L-tyrosine was used to demonstrate the relationship of droplet size and shape on reaction selectivity and to verify computational predictions. By understanding that droplet dynamics affect the yield and selectivity of fast reactions, the formation of byproducts can be minimized by optimizing operating parameters.
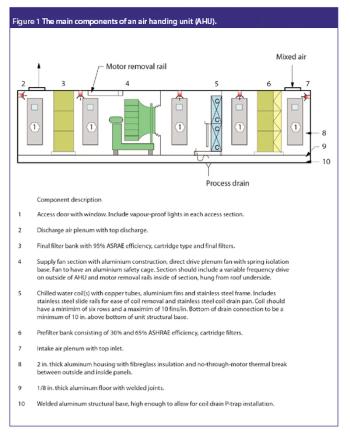
Clean rooms are critical areas in bio/pharma facilities, and it is essential that users are responsible for their care and upkeep, and familiarize themselves with the relevant regulations.
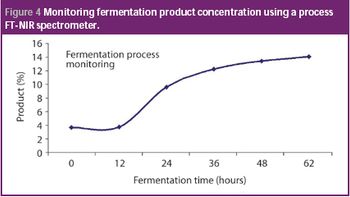
Quality by design and PAT approaches are increasingly being used for the biotech manufacturing of medicines. Complex manufacturing processes can not only be controlled using PAT principles, but optimized with respect to both product quality and economic value. This column describes how the fermentation process is often the first to benefit from this type of implementation.

The ¤9.5 billion therapeutic antibody market comprises over a dozen antibodies that have been generated using recombinant genetic methods developed over the last 20 years.

Robin Hwang, a senior principal scientist at Amgen (Thousand Oaks, CA), led the team that developed the first commercial disposable auto-injector for a biopharmaceutical: a prefilled three-step "SureClick" for delivering Enbrel (etanercept), a treatment for autoimmune diseases.

The US Food and Drug Administration issued a guidance document to provide manufacturers of biological products (other than blood and blood components) with its current thinking on reporting requirements on deviations from current good manufacturing practices for biological products.

New York (Oct. 9)-Pfizer has positioned itself to enter the DNA-based vaccine market with its agreement to acquire UK-based PowderMed Ltd., which holds a pipeline of DNA-based influenza vaccines currently in clinical development for treating both seasonal and avian flu.

Rockville, MD (Sept. 28)-The US Food and Drug Administration has released the draft guidance for industry ?Characterization and Qualification of Cell Substrates and Other Biological Starting Materials Used in the Production of Viral Vaccines for the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases.?
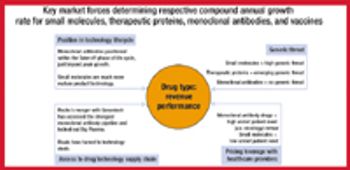
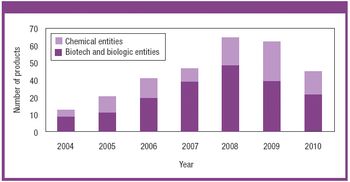
Biologics are forecast to account for roughly 60% of revenue growth through 2010 for Big Pharma as growth in small molecules slows. The author analyzes the factors driving demand and how the technology life cycles of these two sectors will affect market potential.
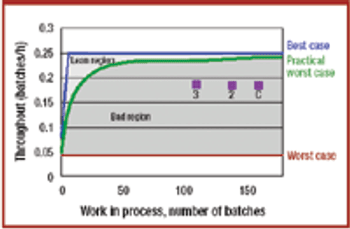
Pharmaceutical companies are facing increased competition, cost pressures, and a need to improve the performance of their manufacturing operations. Lean manufacturing offers methods, tools, and heuristics for improved efficiency in manufacturing. Process analytical technology offers alternative analysis techniques that could greatly improve manufacturing quality and efficiency. Mathematical tools exist for assessing the efficiency of manufacturing processes. Internal benchmarking is recommended for determining the efficiency and tracking improvements in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Protein formulation specialists have long sensed that something big could be just around the corner. Over the past few decades, countless companies have attempted to bring to market new protein therapeutics that offer improvements-be they more patient friendly, more effective, or easier to manufacture-over traditional formulations. Earlier this year, the launch of Pfizer's "Exubera" pulmonary insulin met this anticipation head on. The fast-acting, inhaled-powder form of recombinant human insulin brought hope to the millions of diabetic patients waiting for an alternative to injections.
There is a growing need for patient-compliant dosage forms within the cancer therapeutics and biotechnology areas. Ease of administration, enhanced therapeutic efficacy, and reduced side effects are factors that differentiate drug delivery products from conventional dosage forms and provide a competitive advantage. This article reviews salient trends in the parenteral drug delivery sector within the realms of a changing regulatory environment, drivers to growth, and recent advances in this field. Challenges associated with bringing parenteral drug delivery concepts to commercialization are discussed.

In view of the nature of its complexity, it might be desirable to apply FDA's process analytical technology to lyophilization.
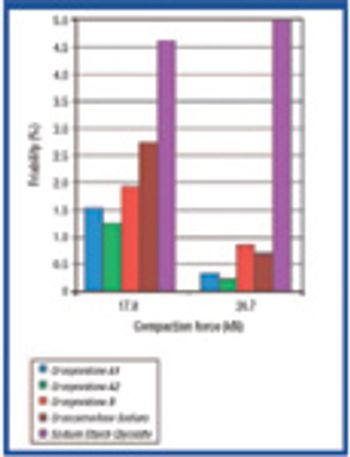
The increasing popularity of orally disintegrating tablets has led to growing interest in the advantages of superdisintegrants. This article presents some practical considerations in selecting these ingredients.

UK science has an outstanding record and we remain strong internationally in terms of achievement, productivity and efficiency.

High-containment manufacturing for highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs) represents a niche, but growing niche, in API manufacture. Strategies on serving this sector were discussed at a recent program, ?High-Potency Active Ingredients: Realizing the Opportunities,? organized by the Drug, Chemical, and Associated Technologies Association (Robbinsville, NJ) in conjunction with Pharmaceutical Technology.

The market potential for high-potency active ingredients will be influenced by growth patterns in the cytotoxic drug market. Strong growth is projected for cytotoxics through 2009, but the market then will see generic drug erosion, according to Sarah Terry Johnston, vice-president, healthcare, Datamonitor PLC.

As with pharmaceutical manufacturing as a whole, a risk-based approach is important in manufacturing highly hazardous or potent compounds. Industry groups are working with US Food and Drug Administration (Rockville, MD) to develop a baseline guide for a risk-management approach to determine containment controls required to minimize cross contamination.

Scientists from GlycoFi, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Merck & Co, in collaboration with Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, have engineered yeast cells capable of producing a broad range of recombinant therapeutic proteins with fully human sugar structures (glycosylation).

The overall market size of the Southeast Asia region totals $7 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of about 13% through 2010.

For once, casting originators against generic players might end up strengthening the industry across the board.

As the pace of product development accelerates, the approach to dissolution-method development must advance beyond a manual method and an assay. A natural progression of the method-development process must include the transfer of the manual method onto automated instrumentation.

Potent-compound awareness training for operators is important to understand why the containment and controls are in place.

Washington, DC (Aug. 14)?A new report issued by the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America identifies 418 drugs and vaccines developed through biotechnology. All of the biotechnology medicines and vaccines are now in clinical trials or awaiting approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (Rockville, MD).