
The EIP process addresses the problems encountered with numerous questionnaires when qualifying excipient manufacturers.

The EIP process addresses the problems encountered with numerous questionnaires when qualifying excipient manufacturers.

The crystalline structure of pharmaceutical solids can sometimes be altered during processing. X-ray powder diffraction and near infrared spectroscopy can be used to determine the amorphous and crystalline content of a model substance. The two techniques' precision, accuracy, detection limit and the speed of analysis are compared.

Company Notes: Gibraltar expands facilities; Allozyne appoints new president and CEO, more.

The senior director of Oracle's Life Sciences Business Unit tackles some of the technical issues regarding regulatory standardization, software integration, and the trend toward visualization, among other things.

Company and People Notes: ImClone, BMS, and Merck form agreement; CRI Worldwide names new CEO, more.

Company and People Notes: Orexo acquires Biolipox, Avalon cofounder resigns, more...

An exclusive licence agreement has been signed to develop a new oral treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a condition that affects approximately 165 million people.

CPhI Worldwide, the large trade show of suppliers of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), intermediates, and excipients, took on a decidedly international presence.

Company and People Notes: Novartis and MIT to study continuous processing, GSK appoints Andrew Witty as CEO, more.

The European Fine Chemicals Group (EFCG) issued a position paper on excipients used in pharmaceutical manufacturing at CPhI Worldwide last week.

Company and People Notes: Thermo Fisher Scientific buys Priority Solutions International, Wyeth elects new president and CEO, more.

As China emerges as a significant supplier of pharmaceutical ingredients, it must assure other countries of the safety of its excipients.

A roundup of news from exhibitors at CPhI Worldwide.

Transdermal delivery takes up once-forbidden compounds, reviving markets and creating formulation opportunities.

Amidst debate, the European Pharmacopoeia Commission is working to include physical or "functionality-related characteristics" of exipient materials in its monographs.

To monitor and control processes or products, analytical methodology must be fit for purpose. An approach to apply quality by design principles to the design and evaluation of analytical methods has therefore been developed to meet these needs. This article features a downloadable template on which to conduct a failure mode effect analysis (FMEA).
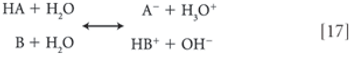
Through consideration of the ionic equilibria of acids and bases, one may readily calculate the formation constant of a salt species solely on the basis of knowledge of the pKA value of the acid and the pKB value of the base.

Orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) continue to attract attention as an alternative to conventional oral dosage forms.
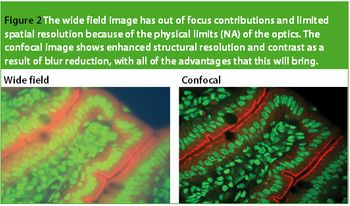
In the biological arena, new and highly useful fluorescent markers are used to stain or 'label' specific structures of interest. They have transformed the range and applicability for optical observation. These labels are excited and correspondingly emit at specific wavelengths; thus, different facets of a specimen can be 'selected' by controlling the wavelength of the delivered and captured light. For example, labels such as 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) are used to highlight the nucleus of a cell and MitoTracker Orange is used for mitochondria. Figure 1 shows an example of a multiple stained section, viewed in fluorescence. There has been an explosion in fluorescent labels for examining biological structures, in fixed and live cell preparations.

High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful tool for the enantioselective separation of chiral drugs. However, the selection of an appropriate chiral stationary phase (CSP) and suitable operating conditions is a bottleneck in method development and a time- and resource-consuming task. Multimodal screening of a small number of CSPs with broad enantiorecognition abilities has been recognized as the best strategy to achieve rapid and reliable separations of chiral compounds. This paper describes the generic screening strategy developed at Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development to successfully develop enantioselective HPLC methods for chiral molecules of pharmaceutical interest.
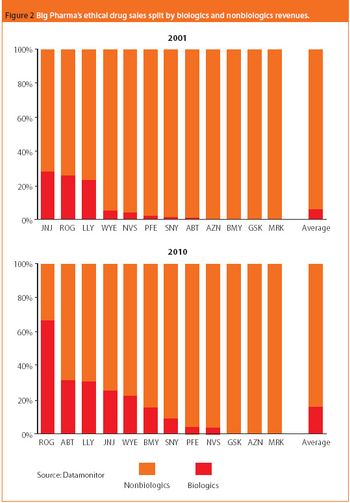
In 2007, the global pharmaceutical market is expected to grow moderately while biologics, generic drugs, and specialty-initiated drugs are projected to increase at double-digit rates. These trends for finished pharmaceuticals are reflected in the global market for APIs, where the merchant generic API market is expected to see strong demand. On a production basis, India and China are forecast to raise their shares of the global generic API market against industry strongholds Italy and Spain. Meanwhile, the US is expected to hold its its position as the leading producer of biotechnology-based APIs in an area traditionally dominated by captive production. And biogenerics or biosimilars gradually reshape the market.
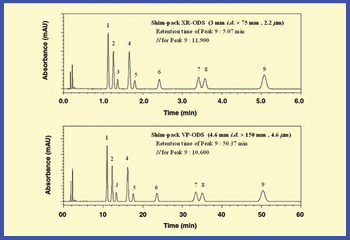
The authors review methods for reducing analysis time and increasing throughput that are reliable and maintain data integrity.
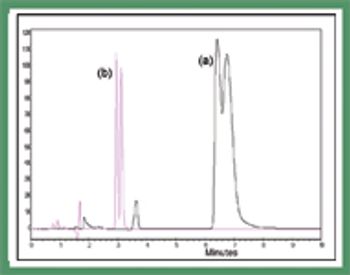
Polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases have been developed that comprise chiral selectors immobilized on their support rather than being physically coated. These materials are completely solvent stable, thereby increasing selectivity and and enabling the development of new chiral selectors that have been too unstable in a coated form for general use.

The combination of supercritical fluid chromatography with chiral separation media offers several analytival advantages over traditional liquid chromatography techniques.
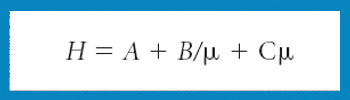
Ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography maximizes efficiency, but, as defined by the resolution equation, the stationary phase is still a crucial consideration when attempting to resolve mixtures of compounds.