
Company and People Notes: Baxter and Halozyme Expand Relationship, Crucell Names COO, More.

Company and People Notes: Baxter and Halozyme Expand Relationship, Crucell Names COO, More.

More than 100 people attended this week’s Regulatory Affairs Conference by the International Pharmaceutical Excipients Council of the Americas to discuss the latest trends and challenges in the excipient supply chain.

Aptuit expands its drug-development capabilities with the formation of Aptuit Laurus to take advantage of the growing pharmaceutical outsourcing market in India.
Researchers forward approaches for catalytic hydroformylation, asymmetric hydrogenation, and biocatalysis to achieve enantioselectivity.
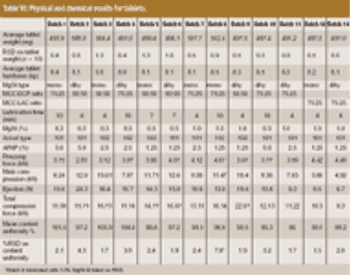
The influence of magnesium stearate (MgSt) on powder lubrication and finished solid-dose properties presents big challenges to drug manufacturers.

This article presents collaborative positions among excipient manufacturers, drug product manufacturers, and members of the US Pharmacopeia on key issues pertaining to the control of pharmaceutical excipients stemming from a recent Pharmaceutical Quality Research Institute workshop.

Fiera Milano Rho Exhibition Centre, Milan, Italy 2–4 October 2007

The recently published Orange Guide 2007 contains significant changes to the GMP requirement placed on pharmaceutical manufacturers, but there have been additional changes to good distribution practice that should not be overlooked.
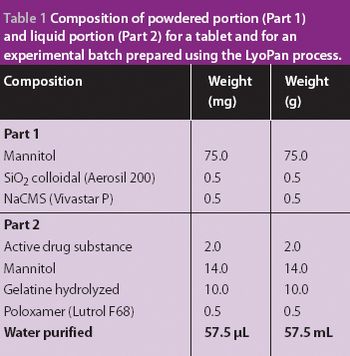
A new economical method for producing fast-melting lamina-like dosage forms.

The authors discuss how companies facing ever-evolving regulatory requirements can address and assess compliance risk in their operating practices.
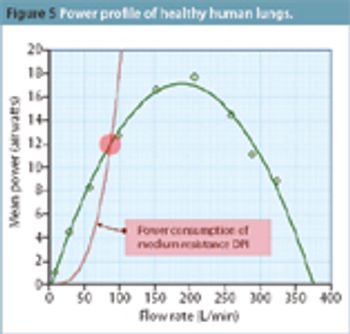
This article investigates how the industry can test inhalers in a way that is most representative of typical use.
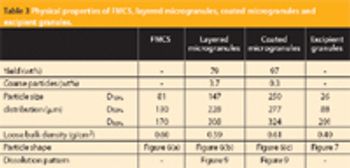
This article describes how rapidly disintegrating tablets containing a large quantity of an intensely bitter drug were successfully developed with a suitable level of masking, tablet hardness, disintegration property, dissolution profile and mouth feel.

A new Raman spectroscopic method to detect magnesium stearate in powder blends and tablets is described. High-volume pharmaceutical manufacturing requires the use of lubricants to facilitate tablet ejection from compressing machines. However, lubricants may also bring a number of undesired problems that have been widely documented in pharmaceutical scientific literature. New analytical methods are needed to understand lubrication and provide process knowledge in support of FDA's process analytical technology initiative. The detection of magnesium stearate in lactose, mannitol, corn starch and other commercially important excipients is reported. The Raman spectroscopic method has a detection limit of about 0.1% (w/w) based on the 2848 cm-1 band that corresponds to the symmetric stretch of the methylene group in magnesium stearate.

The authors evaluate the scalability of foam-granulation technology using continuous foam addition in high-shear granulation equipment at the laboratory, pilot and manufacturing scales. Immediate- and controlled-release model formulations were used. Continuous and batch addition of foam were compared for the controlled-release model formulation at the manufacturing scale, and physical testing was performed on the granules and finished tablets.

As China emerges as a significant supplier of pharmaceutical ingredients, it must assure other countries of the safety of its excipients.

Identifying polymorphs is a crucial part of the drug-development process as researchers forward select methods to improve detection.

Contract manufacturers and pharmaceutical ingredient suppliers proceed with select investments in biologics manufacturing, small-molecule synthesis, and formulation as the industry prepares for CPhI Worldwide in Milan.

Single-enantiomer drugs represent an increasingly large share of new chemical entities, leading to approaches in asymmetric synthesis.

Irish researchers have developed a method that could be used to deliver controlled amounts of drugs to diseased tissues while minimizing side effects by shining light on the target.

A spate of drugs are scheduled to come off patent, offering vast potential and competition.

The company begins production at a new $100-million manufacturing facility for prefilled injection systems, plans further investment in packaging facilities, and targets both early-phase development and commercial manufacture.
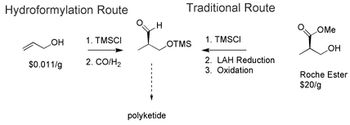
Catalytic routes to producing atorvastatin and sitagliptin are recent advancements.

During the past 30 years, manufacturers developed sophisticated packaging and delivery systems to support the requirements of traditional and complex biologics, including quality and cleanliness. This article discusses the evolution of packaging and delivery systems for injectable administration systems as the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry evolved during the past 30 years. It also explores the future of packaging and delivery systems as technology and drug development advance.

Catalytic routes to producing atorvastatin and sitagliptin are recent advancements.

The author reviews advancements in formulation that Pharmaceutical Technology has chronicled during the past 30 years. During this time, many novel solutions were investigated and finally became common and accepted techniques. The author also looks ahead to future developments in formulation and drug delivery methods.