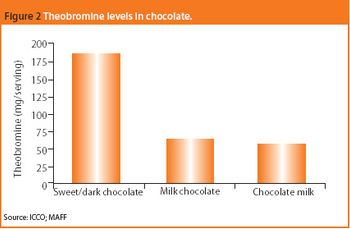
Could compounds in chocolate yield new pharmaceutical approaches to major disorders?


Could compounds in chocolate yield new pharmaceutical approaches to major disorders?
All sectors of manufacturing are under continual pressure to bring new products to market quicker, stealing a march on the competition and maintaining their revenue stream.
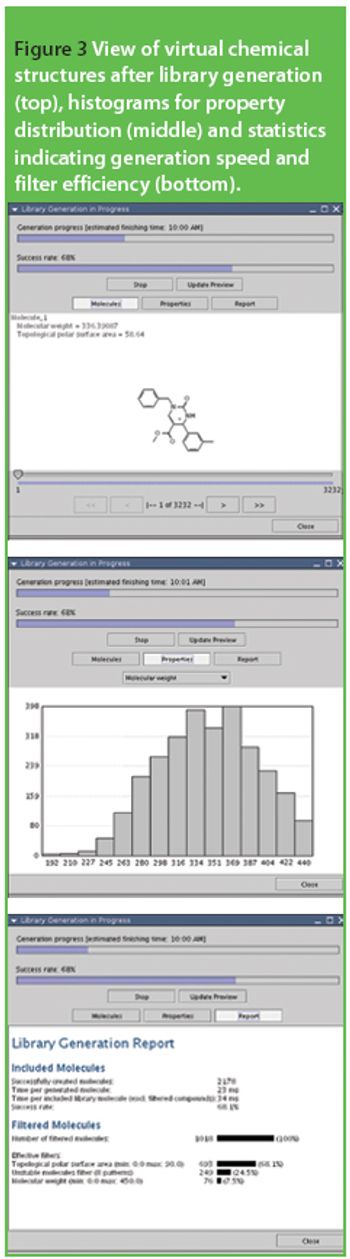
The discovery of suitable lead structures for new drugs from an inexhaustibly large reservoir of theoretically possible compounds is one of the biggest challenges for the pharmaceutical industry. In the last few years, combinatorial chemistry methods have been developed to synthesize a huge amount of diverse new chemical entities (NCEs), which may subsequently be tested for biological activity in vitro.
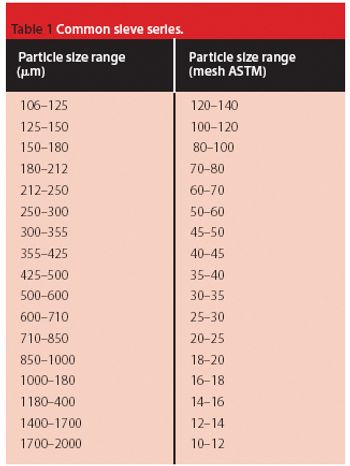
Pellets are a multiparticle, solid form of medication. The individual pellets are almost spherical with diameters usually between 100 and 2000 ?m.

New Biodegradable Polyketals Developed for Drug Delivery

Facing still-sluggish market conditions and a changing world order in fine chemicals, the large Western custom manufacturers are responding by building their toolboxes in specialized technologies in chiral chemistry, catalysis, and biosciences and by adjusting their manufacturing networks via streamlining or investment in Asia.

Adding a cleaning step to the field-testing protocol, and combining it with the data generated to register sanitizing and disinfectant agents under FIFRA and the CEN TC 216 work program, produces a sanitation-and-disinfection validation methodology that is cost-effective, simple, and time-saving.
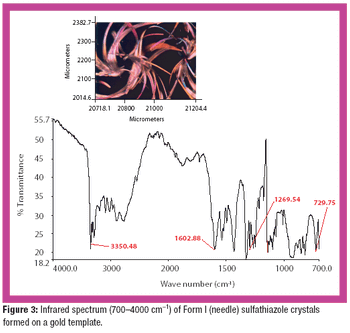
Polymorph farming on a chip is a promising strategy for rapid polymorph discovery by transforming crystallization?crystal isolation?characterization into one time-efficient step.
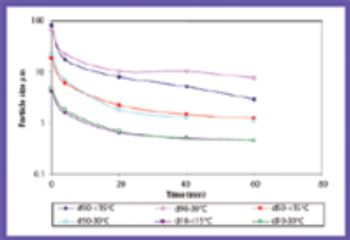
A modified modular high-pressure system can form nanosuspensions of model compounds by individually controlling cavitation, impact, and shear forces.
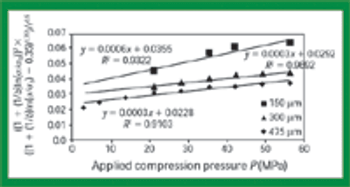
Quantitative data from the literature show strong relationships among average particle size, powder densification, tensile strength, and hardness.

Letter to the Editor: Glen Jon Smith
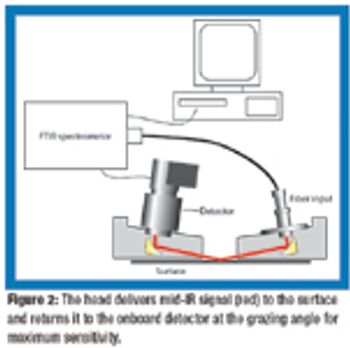
Analytical tools and methods that require less water and detergent are gaining interest for faster, more efficient cleaning.

Human plasma provides a rich source of therapeutic medicines, including gamma globulins, coagulation factors, albumin, alpha anti-trypsin and others. In 2001, sales of immuno gamma-globulin (IgG) were estimated at $2 billion with a production rate of 50 metric tons for the year.1 A number of therapeutic products have been introduced including Gammimune from Bayer, RhoPhylac from ZLB Behring and Octagam from Octapharma.

The manufacturing process used for an API’s production is a crucial factor determining its quality.

Warning Letter: Southern Meds

Scientists working at the Scripps Institute have re-engineered an antibiotic drug at the molecular level...
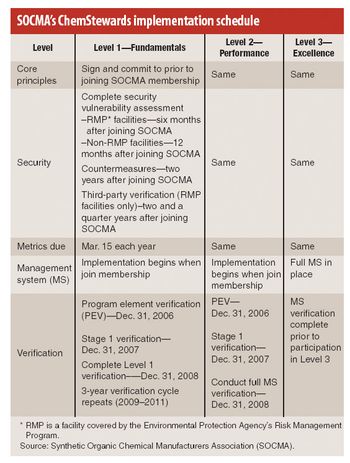
This is a year of change for the Synthetic Organic Chemical Manufacturers Association (SOCMA), the Washington, DC-based trade association representing chemical batch and custom manufacturers. Following the sale of Informex, its flagship trade show, last fall, the association is advancing key programs, most notably its new ChemStewards program, an environmental, health, safety, and security initiative (EHS&S) that its members began implementing last month.

Although physicochemical preformulation screening is practised universally within the pharmaceutical industry, physicomechanical screening is applied to a lesser extent and often only where a problem exists.

Chewing gum is being developed by Generex as an alternative buccal drug delivery method of metformin for treating diabetes. Results from a small clinical trial, which compared pharmacokinetic profiles of metformin gum with its traditional tablet form, suggest that the gum could additionally avoid the significant adverse gastrointestinal side-effects, including diarrhoea and nausea/vomiting, often accompanying the use of metformin tablets. Given that approximately 30% of metformin users experience such unwanted effects, the gum version could improve patient compliance.

Though dissolution testing has been under scrutiny, it is still a powerful test method.
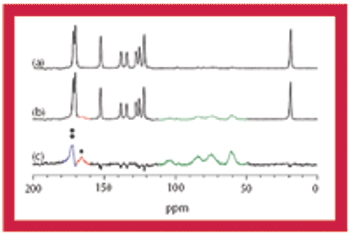
This article discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using solid-state NMR spectroscopy for the analysis of pharmaceutical solids.
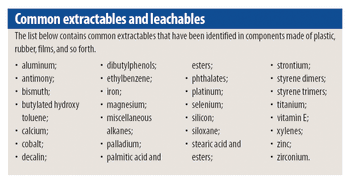
Extractable and leachable issues should be resolved early in the drug manufacturing process. Open communication is imperative for a successful study.
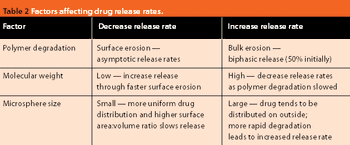
Drug delivery systems using biocompatible polymers allow controlled release of therapeutics, addressing many of the challenges of conventional administration. Polymer microspheres are attractive delivery systems, having a wide application in numerous therapeutic indications. This article reviews the current use and trends for polymer microspheres, and compares production methods and polymer characteristics.
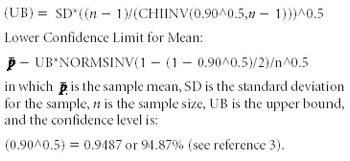
Using the Bergum Method and the MS Excel software program, the author determines the probability of passing the USP dissolution test.

FDA Sees Hike in Combination Product Applications