
Also, GSK expands in Ireland, executive appointments at ProGenTech, more...

Also, GSK expands in Ireland, executive appointments at ProGenTech, more...

MannKind suspended discussions with potential partners for the commercialization of its "Technosphere Insulin" product.

Also, Alcon plans to open Singapore facility, Pharmacopeia president and CEO retired, more...

Also, Jubilant Organosys to acquire DRAXIS Health, PPD's Paul Covington to retire, more...

Also, VaxGen and Raven terminate merger agreement, Darren Head appointed CEO of Cytovance, more...

The former formulation-development business of MDS Pharma Services seeks to build its niche in early-phase drug development.

A reference book omits important information and ignores advanced testing procedures.

The FDA itself issues a cry for help. Is anybody listening?

Companies continue to develop inhaled insulin and other drugs, despite the problems that Pfizer's "Exubera" experienced.

What makes a drug ripe for respiratory delivery?
Monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins have increased their importance and gained success as therapeutic agents in the treatment of various diseases.

As the US biopharmaceutical industry and regulators debate new requirements for biosimilars, industry leaders are turning to analytical science to define intellectual property and business development strategies. Emerging techniques are providing previously unseen protein characterization details, giving both innovator and generics companies new weapons in the battle for future market share.
Biopharmaceuticals are the most rapidly growing segment of the pharmaceuticals market. Developing and marketing biopharmaceuticals are huge roles in almost every major pharmaceutical company's strategy. However, they are extremely complex molecules and are highly sensitive to the manufacturing processes used to produce them. These processes require exquisite control of living production systems, making, without a doubt, biopharmaceuticals one of the most challenging products of any type to manufacture.
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) forms an interface between the circulating blood and the brain, and functions as a tremendously effective barrier for the delivery of potential neurotherapeutics into the brain parenchyma. Conversely, the BBB possesses various carrier-mediated transport systems for the uptake of small molecules, such as essential nutrients and vitamins. These transporters have become an attractive target for drug/prodrug design in an attempt to ferry drug molecules across the BBB. Central nervous system (CNS) drug delivery is often limited by poor brain penetration of the potential drug candidate. As a result of its unique barrier properties, the BBB poses a huge challenge for the delivery of potential neurotherapeutics into the brain parenchyma.1 It is estimated that only 2% of small-molecule drugs and ,0.1% of novel protein and peptide pharmaceuticals developed for CNS diseases reach therapeutic concentrations in the brain.2,3 Many of the pharmacologically active drugs tend to fail..
Our company is involved in developing and manufacturing APIs that can be utilized with drug-eluting stents (DES). Despite ensuring constancy in pharmaceutical composition, we are experiencing issues with variations in drug release during in vitro studies. We are working closely with a stent manufacturer to develop the system, but could surface analysis techniques investigate the problem further?
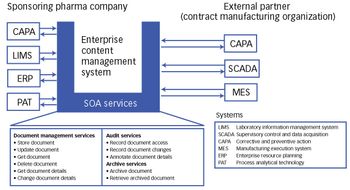
As a skipping stone creates ripples in a lake, SOA can help create benefits that quickly ripple through many other areas of the organization and partners.
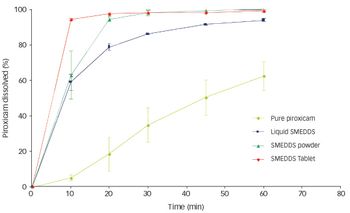
Spraying techniques can be used to produce powder form formulations. The concept works by the adsorption/absorption of a liquid SELF onto a neutral carrier…

A microelectronic system based on radio-frequency (RF) cell ablation addresses limitations of other transdermal drug-delivery methods. This system expands the transdermal spectrum to include the delivery of water-soluble molecules, peptides, proteins, and other macromolecules.

Investigators are exploiting the tremendous structural diversity of polypeptides and their biophysical properties to develop novel drug carriers. Peptide-based materials hold out much promise for tailor-made targeting, penetration, and release of contents in a host of biological microenvironments.

For pediatric and geriatric patients, fast-dissolving drug-delivery systems provide an easier way to take medications and vitamins. Oral thin films have evolved to provide systemic delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients for over-the-counter and soon, prescription drugs. The authors review the practical benefits of dissolvable films, their manufacture, and their market potential.

Liquid and semisolid encapsulation using two-piece hard capsules is an ideal drug delivery approach for highly potent compounds and poorly water-soluble drugs. The authors detail the factors to reduce risk when designing and operating a facility for secondary manufacturing of highly potent drugs.

The nature of their application and their mode of use mean that prefilled syringes meet the regulatory definitions of immediate packaging or container–closure systems.

In a press release, the University of Texas announced that Mauro Ferrari, of the University?s Health Science Center at Houston, presented a proof-of-concept study of a new multistage delivery system for imaging and therapeutic applications.

Also, Alkermes announces restructuring and reduction of workforce, Icagen announces several senior management promotions, more...

Scientists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have successfully tested a new inhaled tuberculosis (TB) vaccine.