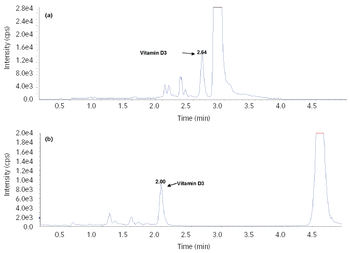
An LC–MS/MS method for the quantitative determination of vitamin D3 in human plasma has been developed and validated with positive atmospheric chemical ionization sources.

An LC–MS/MS method for the quantitative determination of vitamin D3 in human plasma has been developed and validated with positive atmospheric chemical ionization sources.

A new book inspires readers to seek ways to apply NMR spectroscopy to their own purposes.

Michigan State University researchers have discovered a technique for viewing whole cells to gain an understanding of protein inclusion bodies.

A book about pharmaceutical analysis engages the reader with history and unexpected asides.

Efficiency is more than just a buzzword in today's pharmaceutical industry; declining productivity and diminishing returns on investment have made it an over-arching mindset that is critical to corporate survival.
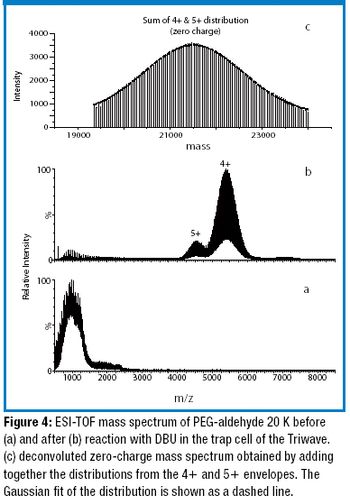
The authors developed a method to accurately measure the average molecular weight of large poly(ethylene glycols) (PEGs) using ion-mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry coupled with gas-phase ion–molecule reactions.

Combining atomic force microscopy and infrared spectroscopy, scientists at the University of Illinois have demonstrated a method for simultaneous structural and chemical characterization of samples at the femtogram (10-15g) level.

My personal experience of lab automation is limited to supervising a peptide synthesiser back in the late 1980s. The machine was eye-wateringly expensive - but it was soon paying its way in terms of productivity and research publications. So if I were a stake-holder in a company pondering whether to invest in a well-designed gadget that could automate a routine operation, I'd say: 'go for it'.

USP 467 Residual Solvents will take effect on July 1, 2008. But does the industry understand these specifications-and is it prepared?

Historically, the main purpose of laboratory information management systems (LIMS) has been to track and manage samples in the laboratory. LIMS originated nearly 30 years ago as a rudimentary method of automating manual, error-prone processes in the laboratory and, with the growth in adoption of technology, became the de facto benchmark for laboratory control and management.

Industry and regulatory organizations agree that the current focus on product quality will play a major role in shaping pharmaceutical development in the future. Key to this assessment of quality are the methods and technologies in pharmaceutical analytical testing.
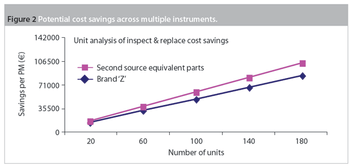
Maintenance and service-related items are often the second-largest budget element in a laboratory after salaries and benefits. Within maintenance, preventive maintenance (PM) is a substantial portion of the budget. Traditionally, PM was an equipment maintenance philosophy based on replacing, overhauling or remanufacturing a piece of equipment at fixed intervals, regardless of its condition at the time. In essence, it involved fixing something that wasn't necessarily broken and this approach is still widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.

High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful tool for the enantioselective separation of chiral drugs. However, the selection of an appropriate chiral stationary phase (CSP) and suitable operating conditions is a bottleneck in method development and a time- and resource-consuming task. Multimodal screening of a small number of CSPs with broad enantiorecognition abilities has been recognized as the best strategy to achieve rapid and reliable separations of chiral compounds. This paper describes the generic screening strategy developed at Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development to successfully develop enantioselective HPLC methods for chiral molecules of pharmaceutical interest.
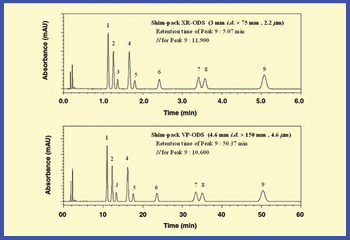
The authors review methods for reducing analysis time and increasing throughput that are reliable and maintain data integrity.
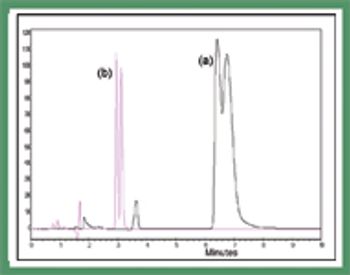
Polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases have been developed that comprise chiral selectors immobilized on their support rather than being physically coated. These materials are completely solvent stable, thereby increasing selectivity and and enabling the development of new chiral selectors that have been too unstable in a coated form for general use.
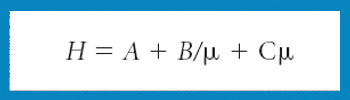
Ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography maximizes efficiency, but, as defined by the resolution equation, the stationary phase is still a crucial consideration when attempting to resolve mixtures of compounds.

A new Raman spectroscopic method to detect magnesium stearate in powder blends and tablets is described. High-volume pharmaceutical manufacturing requires the use of lubricants to facilitate tablet ejection from compressing machines. However, lubricants may also bring a number of undesired problems that have been widely documented in pharmaceutical scientific literature. New analytical methods are needed to understand lubrication and provide process knowledge in support of FDA's process analytical technology initiative. The detection of magnesium stearate in lactose, mannitol, corn starch and other commercially important excipients is reported. The Raman spectroscopic method has a detection limit of about 0.1% (w/w) based on the 2848 cm-1 band that corresponds to the symmetric stretch of the methylene group in magnesium stearate.
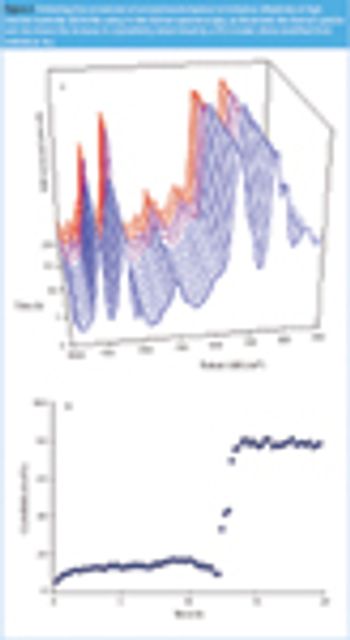
Raman spectroscopy has become a commonly used technique for physicochemical analysis that possesses many advantages over other analytical techniques. It is a very attractive characterization tool, not least because it enables measurements in water. However, very few examples of its application in an aqueous environment exist in literature. This paper provides some recent applications of Raman spectroscopy in pharmaceutical material and process characterization when water is present.
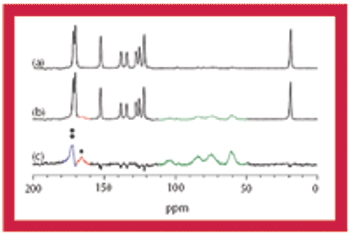
This article discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using solid-state NMR spectroscopy for the analysis of pharmaceutical solids.
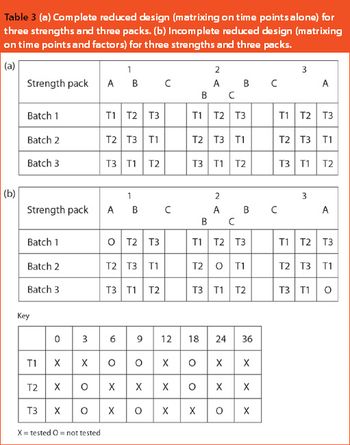
This article looks at the use of bracketing and matrixing to lower the number of stability samples required and, consequently, reduce the cost of sample production, testing and management. There is a common misconception that regulatory authorities will not accept such methods, but there is actually an International Conference on Harmonization guideline (ICH Q1D) on the subject. In fact, many of these designs have already been accepted and FDA members were among the first to describe matrixing.

The first part of this article introduced the basic features of Raman spectroscopy and presented some examples of its application in the pharmaceutical industry. This second part focusses on the technique's application as a PAT tool within the pharmaceutical manufacturing environment. FDA's PAT initiative has provided motivation to explore the application of 'new' analytical technologies to the pharmaceutical manufacturing process and Raman spectroscopy shows great promise. The strengths and weaknesses of the technique as a potential PAT tool are discussed together with some examples of how this works in practice in a pharmaceutical manufacturing environment.

Detection and identification of different polymorphic forms is, therefore, important throughout the drug development and manufacturing process.

Analytical instrument suppliers are developing manufacturing-tailored tools that are small, precise, and easy to use.

Laser diffraction is an important technique for particle size analysis. This article highlights the many advantages this tool has to offer.
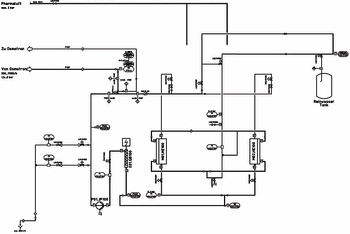
This article describes the quality of highly purified water and its applications, addressing why ultrafiltration (UF) is being used as a downstream purification process. It aims to show that UV is a real alternative for producing pyrogen-free water. This method allows essential cost savings compared with distillation and guarantees a higher safety than other membrane methods such as reverse osmosis.