
FDA funds research to further development of innovative generics, while working to address review and approval issues.

FDA funds research to further development of innovative generics, while working to address review and approval issues.

A new method of vaccine design, called the Multiple Antigen Presentation System (MAPS), may result in vaccines that bring together the benefits of whole-cell and acellular or defined subunit vaccination.

Australian team develops method for making ultrafine particles for more efficient drug delivery.

Susan Schniepp, vice-president of quality and regulatory affairs at Allergy Laboratories and co-chair of the program planning committee for the 2013 PDA/FDA Joint Regulatory Conference, discusses quality systems and related considerations in parenteral drug manufacturing.

Continuous countercurrent tangential chromatography (CCTC) is a column-free process that provides a scalable, disposable, and cost-saving alternative to column chromatography.

New cartridges designed specifically for use on high-speed filling lines increase efficiency.

Molecular Profiles has opened a new facility in the UK following official approval from MHRA.

Report outlines recommended practices for control and evaluation of operations.

Novartis and Biological E, a biopharmaceutical company based in India, have entered into an agreement that aims to deliver affordable and accessible vaccines for typhoid and paratyphoid A fevers to developing countries and thereby address the unmet medical need in endemic regions.

Almac introduces handling and bottling capabilities in EU and US headquarters.

Risk management guides decisions in facility design and operation for highly potent drugs.
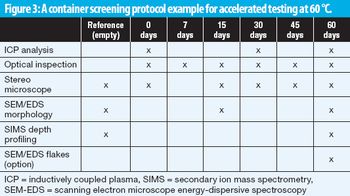
A screening method aligned with USP 1660 guidance predicts glass delamination in primary packaging for parenterals.

Understanding the supply-chain challenge and coupling high-efficiency chromatographic techniques with information-rich detectors are leading to improvements in the management of extractables and leachables in parenteral drugs.

The author presents best practices for extractables and leachables.

GE Healthcare's partnerships with iBio and Brazil's Bio-Manguinhos/Fiocruz for a new plant-based multipurpose biopharmaceutical and vaccine manufacturing facility move plant-based protein production to the next level.

The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use has recommended granting of marketing authorizations for the first two monoclonal antibody biosimilars.

Since its inception in 2011, Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies has added capabilities and single-use production capacity for mammalian-derived product manufacturing, upgraded development and pilot-scale microbial laboratories, and installed advanced analytical instrumentation.

The benefits of single-use systems are being realized for downstream unit operations, including aseptic filling.

Global program seeks to confirm biosimilarity to support regulatory submissions in the US and EU.

A conversation with Kevin Brady of Alkermes about how high potency APIs are changing the way drugs are developed and manufactured in terms of process, equipment and regulations, including a case study that demonstrates the effective scale up or manufacture of a drug with a highly potent API.

A screening method predicts delamination in primary packaging.

Semi-automatic technology aids egg-based influenza vaccine production in smaller facility footprints.

PSL has developed a microsphere refiner for microsphere formulation, from small scale processes to commercial production.

Aseptic connectors provide the flexibility and robustness needed for modern parenteral manufacturing operations.

The lipid-based method provides a tool for delivery of highly potent, poorly soluble, and unstable APIs. And new in-process capsule printing and shell technologies expand softgels’ applications further.