
NIH provides an interim corrective action plan to correct deficiencies found in its Clinical Center Pharmaceutical Development Section.

NIH provides an interim corrective action plan to correct deficiencies found in its Clinical Center Pharmaceutical Development Section.

The agency streamlines risk and mitigation information.

The agency publishes guidance on the physical attributes of generic tablets and capsules.

Presenters at IVT's Microbiology Week discussed best practices and recent guidance publications for microbial control in sterile and non-sterile pharmaceutical processes.

Although full traceability is not required by law in the US until 2023, companies could benefit from implementing it now.

The agency creates initiative to stimulate pediatric drug development.

BPTF seeks changes in performance goals and fee payment schedule in GDUFA renegotiations.

An advisory panel deemed Amgen’s Repatha (evolocumab) to be safe overall.

An FDA advisory panel voted 13-3 in favor of approval of Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals' cholesterol-homeostasis therapy Praluent (alirocumab).

The agency issues draft guidance on the development of drugs to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy.

FDA recently issued a much-anticipated draft guidance on how to define and report established conditions in market applications.

The Hapa 862, from Hapa AG, is a modular, CMYK/spot-color inkjet printing system for the in-line packaging printing of foils and labels.

Agency officials visit China to meet with Chinese regulators and industry representatives about keeping the pharma supply chain safe.

Drug quality issues have forced the National Institutes of Health to shutter its in-house facility for producing clinical supplies for certain clinical trials.

The agency cited VUAB Pharma, located in the Czech Republic, for cGMP deviations.

FDA cites 17 observations including air handling, quality control, and deficient microbial monitoring at NIH’s Clinical Center Pharmaceutical Development Section.

Regulators and industry seek to streamline and harmonize oversight of postapproval changes.

Clearly defined zones of cleanliness must be designed and maintained to prevent product contamination.
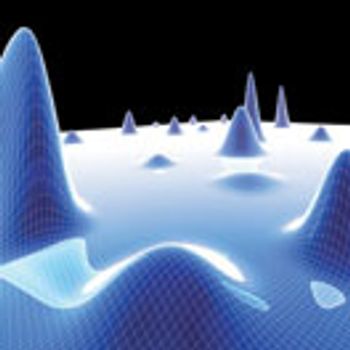
PAT holds the key to real-time quality assurance and consistent product quality in pharmaceutical manufacturing.

The pharmaceutical industry wants to speed up the variations process by eliminating redundant assessment by different national agencies in the European Union.

Will biosimilars share a compendial identity like generic drugs do?

The directorate highlights achievements accomplished during the year of its 50th anniversary.

The restructuring of the International Conference on Harmonization, which is expected to begin in late 2015, could have a significant impact on the way pharmaceutical regulations are harmonized worldwide.

The European Pharmacopoeia addresses the need for monographs for biologicals to keep pace with recent analytical technology advances.

The ICH Steering Committee will meet from June 6–11, 2015 to discuss a variety of harmonization topics.