
Technology's new monthly "Agent-in-Place" column distills true-life cautionary tales from the secret files of Control, a senior compliance officer.

Technology's new monthly "Agent-in-Place" column distills true-life cautionary tales from the secret files of Control, a senior compliance officer.

Commissioner Crawford’s top priority is to restore public confidence in FDA oversight of drug safety and quality.

New Guidance May Speed Generic Approvals

The European Commission has released its second report to the Council and European Parliament addressing the developments and implications in patent law concerning biotechnology and genetic engineering. The study, which centres on the patentability of inventions relating to stem cells, concluded that those capable of developing into human beings, totipotent stem cells, are to be excluded from patentability on the Directives' grounds of human dignity.

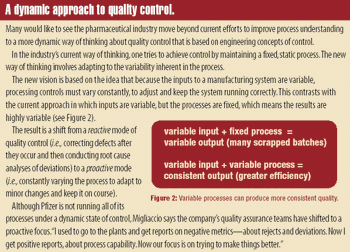
Although new drug development usually focuses on clinical and preclinical research, moving innovative products from clinical testing to market mainly involves overcoming manufacturing capabilities and production challenges. Ensuring access to consistently high-quality critical vaccines and therapies needed to counter bioterrorism attacks is a topic frequently debated. Product shortages are leading to policies that expand US drug and vaccine manufacturing and ensure that US regulatory and healthcare policies avoid erecting roadblocks to high-quality drug production.

Our GMP Agent-in-Place at a top-10 pharmaceutical manufacturing firm reports on a spill during the manufacture of a time-release capsule filled with coated beads.
In 1987, when the US Food and Drug Administration issued its Guideline on General Principles of Process Validation, a young FDA reviewer asked her supervisors.


The question of pharmaceutical pricing is going to be resurrected by the European Commission, despite French President Jacques Chirac's rejection of the new EU treaty. Günther Verheugen, the Commission vice president, made this announcement at the annual meeting of the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associates in Brussels (Belgium) responsible for competitiveness.

Reading the good automated manufacturing practice (GAMP 4) guide acquaints you with the now classic and almost famous V-model.1 The V-model, originally used for describing a validation workflow of IT and automated systems, is easy to understand and very good at ensuring that the requirements and design are built into the final solution. It is also extremely versatile and can be used for almost any type of validation task you could meet in a development phase.

Proposals to expand drug adverse event monitoring will publicize emerging safety concerns and strengthen post-marketing compliance efforts.

Officials at the US Food and Drug Administration are working with industry and academia to develop more efficient and reliable drug production processes that can ensure a consistent supply of high-quality therapies. A modern manufacturing system based on harmonized regulatory policies across global regions is critical for meeting public demand for safe and effective medicines, while also reducing production costs and eliminating waste.

New Excipient Guidance Doesn?t Fill Regulatory Gap

FDA is finalizing guidances and enforcing compliance with manufacturing standards as part of its efforts to ensure drug safety.

Managers of FDA-regulated firms must be proactive in how they manage their company?s compliance with good manufacturing practices regulations.

Innovators and generics makers are staking out positions on follow-on proteins and other manufacturing issues.
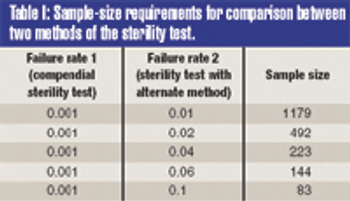
The validation of alternative microbiological testing is an opportunity for a manufacturer to decrease the amount of time required for laboratory results. To properly validate these alternatives, a practitioner must first identify what is being studied. The regulatory effect on established product and process specifications and levels must be completely evaluated, as changing the method of analysis may well change the apparent number in the sample.

FDA Finalizes Guidances on Minimizing Drug Risk and Submitting Pharmacogenomic Data

New fixed-dose combination drugs aim to enhance safety and efficacy, while regulators clear a path for more drug–device combination products.

CBER Draft Guidance for Spore-Formers and Plasmid Vaccines

Concerns about risky medicines may reduce pressure to expand drug imports while boosting demand for more comparative analyses of therapies.

Safety issues and shortages may slow down new drug development and FDA reforms

Blockbuster drugs turn out to be risky business, while contamination problems shut down flu vaccine production.

Defenders of the research-based industry are hoping for an early Christmas present from the European Court of Justice (ECJ). All the signs are that a small but significant victory is on the way against parallel importing. Right at the end of October, a senior judge responsible for a leading case at the court made clear his view that international drug firms do not necessarily have to make life easy for parallel importers. The formal ruling on the case at issue is expected within weeks.

This article provides guidance for minimally acceptable method validation practices and a foundation for assessing the risks and benefits associated with method validation programs.