
Nanotechnology is emerging as a tool for resolving challenges in delivering poorly water soluble and highly potent drugs.

Nanotechnology is emerging as a tool for resolving challenges in delivering poorly water soluble and highly potent drugs.
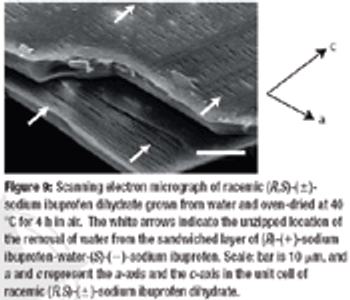
The racemic compound (R, S)-(±)-ibuprofen is a popular and well understood active pharmaceutical ingredient, but it has several disadvantageous formulation properties such as poor solubility, low melting point, and potential esterification with excipients containing an hydroxyl group. The authors investigate the use of an (R, S)-(±)-ibuprofen salt to evaluate these problems using various analytical methods to determine the polymorphism, crystallinity, and drying scheme.

Exhibitors' products prevent counterfeiting, provide child resistance, protect product quality, and improve packaging-line efficiency.

The Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Committee (APIC) - a sector group of Conseil European des Federations de l'Industrie Chimique (CEFIC) - first voiced the need for EU GMP API legislation in 1993 to help ensure the safety of medicines. In 2000, the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) finalized the harmonized API GMP Guideline Q7, which became legal in the US and Japan in 2001. The EU adopted a directive in March 2004 that includes the requirement for APIs in medicines for the EU market to comply with ICH/Q7A. Member States are transposing the directive into their national law: about half of them have completed this process, seven more are well on their way to completion, while seven others are still in earlier stages of adoption.
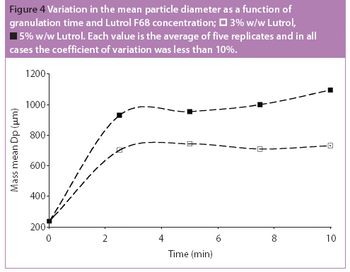
Fluidized hot melt granulation (FHMG) is an emerging technique combining the advantages of both dry and wet granulation methods, and represents an innovative continuous granulation process capable of mixing and agglomerating excipients and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to produce uniform blends of particles suitable for use in the manufacture of pharmaceutically elegant solid dosage forms.
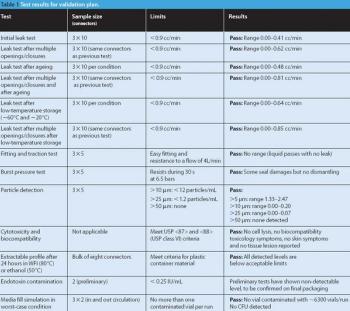
Sterile liquids are frequently transferred during the processing of sterile liquid drugs such as injectables or ophthalmic drops. Several types of transfer can be performed, each requiring a validated method to ensure the desired sterility-assurance levels are achieved.

It has been a long time coming, but stakeholders in the US are now seriously debating a route to market for cheaper copies of biopharmaceutical drugs. The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products (EMEA) has led the way on this issue by publishing clear guidelines on what companies must do to get their versions of drugs such as erythropoietin (EPO), an advanced treatment for anæmia, and similar products approved.
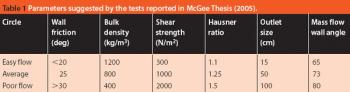
Predicting the flow characteristics of powders during manufacture is especially important for the pharmaceutical engineer. Getting the powder flow wrong can be highly disruptive to plant performance and productivity, particularly where equipment has to be taken off-line and stripped down for cleaning out blockages. The flow behaviour of the individual ingredients may be well known, but as these are blended and reacted their flow properties can change.

Cells function as highly accurate quality control (QC) machines to ensure that only correctly folded proteins are released into the physiological milieu to perform their designated functions. The efficient removal of damaged or incorrectly folded/misfolded proteins at the correct time keeps a cell viable and functioning.


Darmstadt, Germany (May 13)-Mylan Laboratories Inc. and Merck KGaA have signed a share purchase agreement under which Mylan will acquire all of Merck's worldwide operations within Merck Generics, the company?s generics business.

Boston, MA (May 8)-The global biotechnology industry showed several positive signs in 2006, including increases in overall revenues and financing, although the industry as a whole continues to operate at a loss, according to Ernst & Young's annual analysis of the biotechnology industry.

Rockville, MD (May 1)-The US Food and Drug Administration issued a report, "Critical Path Opportunities for Generic Drugs," to identify the scientific challenges, including those in manufacturing science, in developing generic drugs and the opportunities for collaborative solutions in resolving those challenges.

Washington, DC (April 30)-Less than two weeks after the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee voted to reauthorize the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA), the bill this week moved onto the Senate floor.

Geneva, Switzerland (Apr. 27)-A meeting of the World Health Organization and the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use's approval of Novartis's new cell culture-derived influenza vaccine offered new hope that sufficient numbers of vaccines could be produced in case of a pandemic.

There is a tremendous need to enhance delivery of potential therapeutics to the brain for treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders. The blood brain barrier (BBB) restricts and controls the exchange of compounds between the CNS and the blood, which requires discovery of new modalities allowing for effective drug delivery to the CNS. Polymer nanotechnology has now become one of the most attractive areas of pharmaceutical research. This review focuses on the current progress in polymeric nanoparticles, where the specific arrangement of the polymeric matter at the nanoscale is utilized to design drug delivery systems that provide safe and efficient transport of CNS drugs across the BBB.

This article discusses a number of factors that may influence the behaviour of conjugated biopharmaceuticals. Optimizing bioconjugation processes may be critical to achieve the desired drug performance.

One of the major concerns with introducing PAT, however, is that the bias towards process engineering may not ultimately lead to complete control of product quality.

...Scotland has a favourable regulatory environment, funding support from its government and some of the most advanced research facilities in the world.

Green chemistry involves redesigning processes so that more of the raw material ends up in the product, rather than as waste...

Interphex2007, New York, NY (Apr. 25)-As governments begin to contemplate the possibility of biological terrorism or a pandemic event, a new problem begins to emerge: in the case of a pandemic or an attack, even if a vaccine or treatment exists, how could it be produced in sufficient numbers to prevent the deaths of millions of people? That question was addressed in at the conference session, "Responding to Bioterrorism and Pandemic Events: A Case for Development of Flexible Manufacturing Space for Vaccine Production," at Interphex today.

Lyon, France (Apr. 17)-Sanofi Pasteur, the vaccine division of the Sanofi-Aventis Group, announced that the US Food and Drug Administration has licensed its H5N1 vaccine, making it the first avian-influenza vaccine for humans in the United States.
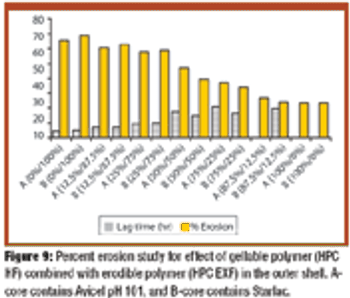
The authors prepared and tested press-coated tablets with various weight ratios of ethylcellulose to hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) and various ratios of two different batches of HPC as an outer coating shell and fillers in core tablets. The tablets were examined for changes in time lag and release patterns of salbutamol sulfate.
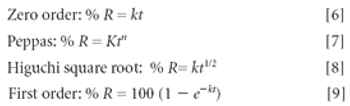
Hydrogels are biocompatible drug delivery systems by which the physical properties can be controlled by the cross-linking density. Hydrogels were prepared by copolymerization of acrylic acid monomers in the presence of poly(ethylene glycol)(PEG) to form polyethylene diacrylate (PEDGA). Various molecular weights of PEGs were used for the synthesis of PEGDA to study the effect of molecular weight of PEG on the properties of hydrogels. These hydrogels were further characterized for free water, swelling behavior, water diffusion, drug loading, and drug release profile. By analyzing the swelling behavior and release pattern of the hydrogels, the authors show that these systems can be suitably used for controlled delivery of drugs.
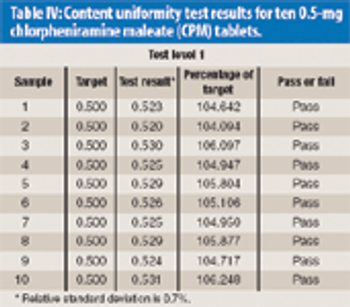
Near-infrared (NIR) assay and content uniformity of tablets provide fast, accurate means of monitoring tablet production that are in step with FDA's process analytical technology initiative.The authors discuss the process for testing a newly released NIR tablet analyzer to determine instrument precision and accuracy using chlorpheniramine maleate tablets.The data show promising results that could relieve laboratory workload of high-performance liquid chromatography analysis and bring analysis closer to real time for process monitoring.