Process and Scaling
Latest News


Able Interim Chief Resigns Amid Drug Recall

Police and protests at BIO 2005.

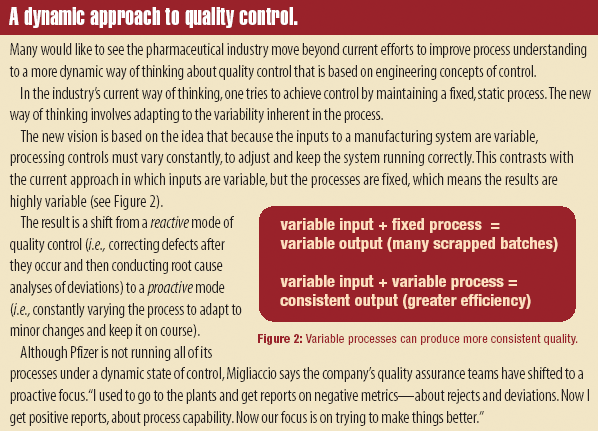
A stepwise, process risk-assessment approach can facilitate the identification and understanding of critical process parameters, quality attributes, and in-process controls. This approach can lead to more use of science- and risk-based regulatory practices to simplify the regulatory requirements for changes to synthetic processes and to support the underlying quality systems that ensure compliance.

Warning Letter: Pragmatic Materials

Warning letter: C&M Oxyfill

In his Feb. 2005 viewpoint article, "In Defense of Singlet Testing," Torbeck (1) draws an important philosophical distinction between "standards" and "specifications." He argues that specifications are criteria selected by manufacturers for statistical control of their products, whereas compendial standards are absolute requirements. This distinction is entirely compatible with modern concepts of statistical process control.

Purdue?s RFID Pedigree Program Enters Pilot Phase

Glossary of computer and software terms.

Nearly eight years have elapsed since the US Food and Drug Administration's 21 CFR Part 11 regulations on the use of electronic records and electronic signatures went into effect (1). In Sept. 2003, FDA issued a guidance document covering the scope and application of Part 11, which described how the agency intends to interpret and enforce the requirements during its ongoing re-examination of the regulations (2). Many in the pharmaceutical industry view the guidance as a positive development that will lead to a simplified FDA approach to Part 11 and a significant reduction in the industry's compliance burden. But this shift in FDA's interpretation and its intended use of enforcement discretion has not ended the controversy and confusion surrounding Part 11 and its requirements.

The use of quality management software (QMS) to automate manufacturing quality processes quickly is becoming an industry-wide initiative. Companies are turning to commercial off-the-shelf systems (COTS) to simplify implementation and validation efforts. Regardless of the system selected, the automation of these critical quality processes is subject to electronic records and electronic signatures (ER/ES) requirements, as set forth in the 21 CFR Part 11 regulation (1). Therefore, companies must adopt a comprehensive but manageable approach to Part 11 compliance as they begin to automate the processes that support product quality and efficacy to ensure they meet the requirements of good manufacturing practices and all predicate rules.
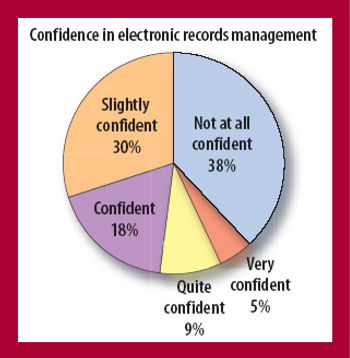
Pharmaceutical firms have every reason to feel confused and even a bit bewildered by what the US Food and Drug Administration expects from them when it comes to controlling electronic records. At times over the past nine years it has been a bit like riding a roller coaster that you weren't allowed to get off.
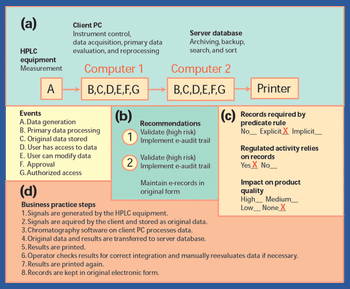
In 1997, the US Food and Drug Administration issued a regulation"Rule 21 CFR Part 11," that provides criteria for the acceptance of electronic records, electronic signatures, and handwritten signatures (1). FDA issued the guidance in response to requests from the industry. With this regulation, electronic records can be equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures. The rule applies to all industry segments regulated by FDA that include good laboratory practice, good clinical practice, and current good manufacturing practice.
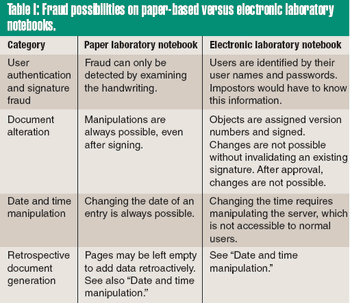
Paper notebooks are the accepted method for recording laboratory data and the ideas generated from that information in the pharmaceutical, biotech, and chemical industries. Nonetheless, the revolution in digital data processing has improved the way data is created, organized, and managed electronically, whether in the form of analytical data, images, documents, or multimedia files. The preservation of such information into a digital form offers the potential for online storage and retrieval, efficient search processes, and worldwide data transmission.

New Excipient Guidance Doesn?t Fill Regulatory Gap

Recalls, Resignations, and Suspended Manufacturing Plague Able Labs

Compounding Pharmacies' Lawsuit Against FDA Will Continue

FDA Drug Safety Oversight Board


Bedford Recall

GSK and FDA Agree on Consent Decree

The unit-dose bar coding rule requires integrating many aspects of packaging design and control.

FDA is finalizing guidances and enforcing compliance with manufacturing standards as part of its efforts to ensure drug safety.

A newly developed software program transforms written SOPs for all required analytical method validation experiments into transferable automated templates, integrating individual activities and technologies under one platform.

Major pharmaceutical companies are focusing more than ever on the prices CROs are charging for their services.