
Nanotechnology is emerging as a tool for resolving challenges in delivering poorly water soluble and highly potent drugs.

Nanotechnology is emerging as a tool for resolving challenges in delivering poorly water soluble and highly potent drugs.

Reflecting strong growth prospects for certain biologic-based drugs, the biotechnology and pharmaceutical majors are proceeding with a strategy of expanding their internal manufacturing networks and partnering with select contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs).

Excipients facilitate formulation design and perform a wide range of functions to obtain desired properties for the finished drug product. The article reviews excipient development and functionality of these materials, including their importance in formulation design, potential processing challenges directly related to excipients, and therapeutic benefits.

The pharmaceutical majors build their capabilities in peptide technology, and contract manufacturers expand to meet growing demand for bulk peptides.

San Juan, PR (Apr. 25)-Regulatory and quality issues were prominent discussion topics at this year?s ExcipientFest conference and exhibition.

Brussels, Belgium (Mar. 22)-The European Commission?s (EC) Directorate-General for Enterprise and Industry (Brussels, Belgium) is asking manufacturers, distributors, and users of human-pharmaceutical excipients to participate in an online questionnaire on the effect of various policy options. Responses will be used to prepare a directive on good manufacturing practices (GMPs) for certain excipients.
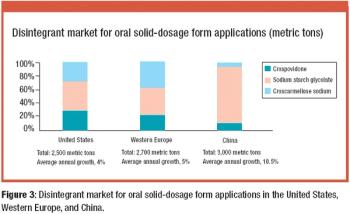
China creates a potential outlet for specialty excipients as its pharmaceutical market grows.

The pharmaceutical supply chain lengthens as generic drug manufacturers build production platforms offshore and CMOs position in India and China to meet demand for lower-cost production.

As custom manufacturers gather for InformexUSA this month, strategies in asymmetric synthesis and catalysis prevail.
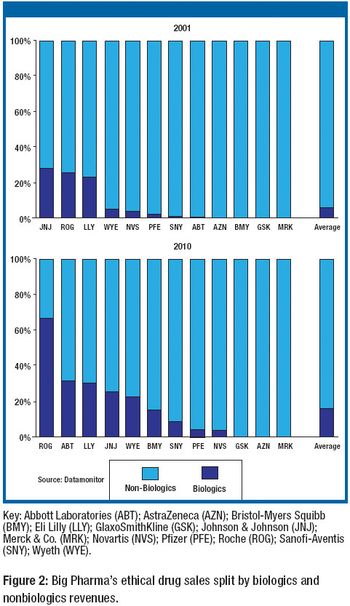
In 2007, the global pharmaceutical market is expected to grow moderately while biologics, generic drugs, and specialty-initiated drugs are projected to increase at double-digit rates. These trends for finished pharmaceuticals are reflected in the global market for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), where the merchant generic API market is expected to see strong demand. On a production basis, India and China are forecast to raise their shares of the global generic API market against industry strongholds Italy and Spain. Meanwhile, the United States is expected to hold its its position as the leading producer of biotechnology-based APIs in an area traditionally dominated by captive production. And biogenerics or biosimilars gradually reshape the market.

AAPS, San Antonio (Oct. 31)-Excipient manufacturers are raising concerns over recently adopted European guidelines, set to become effective January 1, 2007, which provide a framework and approach for dealing with genotoxic impurities in new active substances.

AstraZeneca's purchase of Cambridge Antibody Technology and Merck's acquisitions of GlycoFi and Abmaxis are the latest efforts by pharmaceutical majors to build critical mass in biologics capabilities.
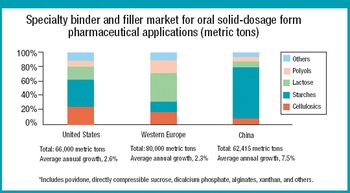
The specialty excipients market in the United States, Western Europe, and China is valued at nearly $800 million. The authors discuss the opportunities and challenges in these markets by examining the product mix, supply base, and preferred production methods.

The authors investigated the influence of various particle size fractions of Tamarind seed polyose (TSP) on indomethacin (IND) release from matrix tablets. They assessed the TSP fractions for swelling, density, and flow properties and the IND matrix tablets for tensile strength, friability, and release profile. Release kinetics was evaluated using Higuchi and Peppas equations. The density and flow properties showed that the size fraction affects the suitability of TSP as an entrapment polymer. The release profile showed that the release of IND from TSP matrix is swelling dependent, thereby affecting the kinetics of release.

As custom manufacturers and pharmaceutical ingredient suppliers gather for CPhI Worldwide in Paris, Oct. 3–Oct. 5, industry observers point to a mixed outlook for pharmaceutical custom synthesis. While industry performance for 2006 is better than 2005, the critical question remains the improvement in drug output. The slow rate of approvals of new molecular entities (NMEs) continues in 2006 as Big Pharma seeks to build pipelines of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) through acquisitions, including capabilities in biologics.
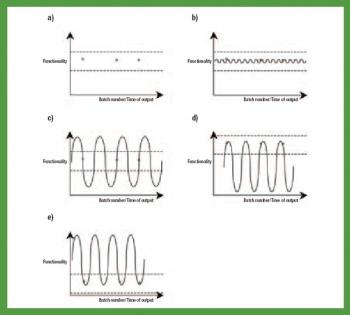
This article provides an overview of functionality, functionality-related characteristics, and excipients performance.
Facing cost pressures and regulatory changes, pharmaceutical companies address the need for increased functionality by looking to excipients.
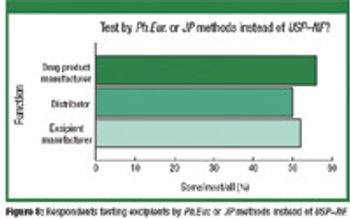
The Product Quality Research Institute (PQRI) conducted an open, publicly available, electronic survey of current excipient-control strategies among pharmaceutical excipient manufacturers, excipient distributors, and drug-product manufacturers (excipient users). Among the major findings are:

Potent-compound awareness training for operators is important to understand why the containment and controls are in place.
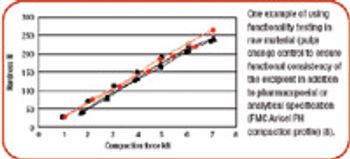
The debate over functionality is not about to be settled anytime soon.

Combinatorial catalysis in asymmetric synthesis and asymmetric biaryl Suzuki coupling highlight recent advances in chiral chemistry. Plus the marriage of green and chiral chemistry.

Select large custom manufacturers expand capacity, private equity firms buy companies in transition, and players from India and China build their positions.
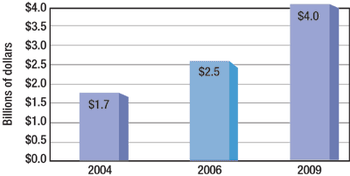
CMOs account for 20–30% of biopharm production. Big Pharma also is filling the biologics supply chain.
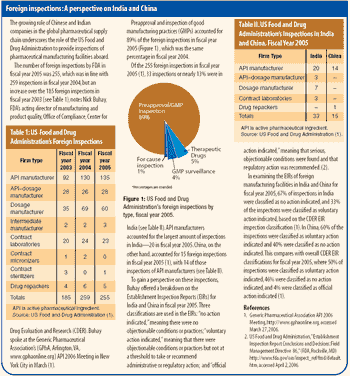
Indian suppliers of active pharmaceutical ingredients and dosage formulations expand in India, the United States, and Europe.

New biocatalytic and chemocatalytic routes to chiral intermediates and developments in simulated-moving-bed and supercritical-fluid chromatography for resolving racemic mixtures.