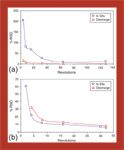
FDA's draft guidance on aseptic processing contains some inherent difficulties, including unrealistic expectations of sterility and microbial quantification, an absence of harmonization with international rules, and failure to support new technologies or a risk-based approach. The authors propose a science-based alternative.