
Pharmaceutical manufacturers that launch ePedigree and serialization initiatives today will improve their competitive positions in the short and long terms.

Pharmaceutical manufacturers that launch ePedigree and serialization initiatives today will improve their competitive positions in the short and long terms.

Drugmakers have many incentives to avoid overfilling their containers, including the scarcity, and correspondingly high cost, of certain cells and ingredients. These concerns highlight the need for techniques that can fill small volumes of product with great accuracy. Many strategies are available to the industry, but which one works best?

Following its $68-billion acquisition of Wyeth, Pfizer is integrating its manufacturing and outsourcing activities (Podcast).

Margaret Hamburg, commissioner of the US Food and Drug Administration, unveiled a new program to improve the efficiency of import inspections.

VaxGen Shareholders Reject OXiGENE Merger; Roche Creates Research Hub In Singapore; And More.

GSK launched a stand-alone unit that will specialize in the R&D and commercialization of medicines for rare diseases.

A highly functioning New Product Planning (NPP) group is a company's first line of defence against losses caused by products that fail to reach the market, according to research and consulting firm Best Practices LLC.

Pfizer's first updated pipeline since its acquisition of Wyeth includes fewer projects than before and is targeted to specific diseases.

Cephalon Buys Mepha; BASi's CEO Retires; and More.

AstraZeneca announced this week that it plans to undertake further restructuring in its research and development operations, resulting in the elimination of 3500 jobs.

Hoping to prevent the deaths of eight million children over the next decade, Bill and Melinda Gates recently committed $10 billion for child-immunization programs in the world's poorest countries.
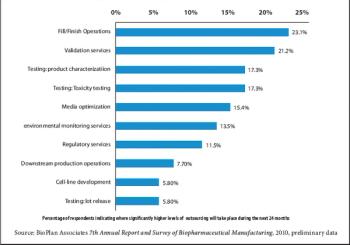
Strategic rather than tactical considerations are driving biopharmaceutical outsourcing.

Sharing too much-or too little-information can have disastrous onsequences.

FDA impersonators and counterfeit drugs threaten the public's trust in online pharmacies.
Editors' Picks of Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Innovations

A look at the formulation challenges in pancreatic enzyme products.

Vaccine R&D is surging, but continues to raise manufacturing and regulatory challenges.

Regulators and industry move to require inspections of API manufacturing facilities.

When it comes to healthcare rform, we must not overlook investment in innovative technologies.
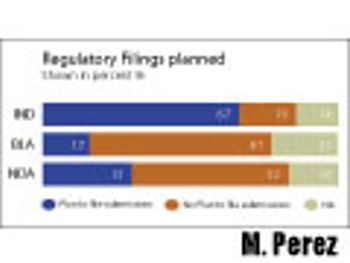
How to cut time and cost by re-using already submitted documents.
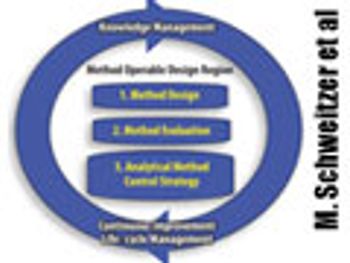
The authors present two concepts to improve robustness and facilitate continuous improvement in analytical methods. This article contain bonus online material.

Leading experts share insight on the current and future direction of process analytical technology. This article contains bonus online material.
We never thought implementing complex changes could become more cumbersome.

The authors present two concepts to improve robustness and facilitate continuous improvement in analytical methods.

Although once used only for large production processes, robotics are now working their way into every aspect of the pharma manufacturing processes.