Visible residue limits have been shown to be a valuable tool in validated cleaning validation program.

Visible residue limits have been shown to be a valuable tool in validated cleaning validation program.

A strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats analysis.

There are many different approaches for assessing process parameter criticality, and assessing which process parameters have a significant impact on critical quality attributes (CQAs) is a particular challenge. Including an unimportant process parameter as a critical process parameter (CPP) in a control strategy can be detrimental. The authors present a statistical approach to determine when a statistically significant relationship between a process parameter and a CQA is large enough to make a practically meaningful impact (i.e., practical significance).

A novel method, based on differential calculus, was used to calculate the maximum potential error associated with the drug concentration in pharmaceutical mixtures composed of an infinite number of ingredients measured on an infinite number of balances with different sensitivities. The method was further applied to calculate the ingredients’ least allowable quantities. This approach ensures that the pharmaceutical formulation is prepared within a given maximum permissible error in drug dose.
The 10-ppm criterion for the acceptable concentration of potential API in cleaning validation to minimize cross contamination into next product has been employed for many years. This article describes why the 10-ppm criterion, which was established based on analytical limitations and estimates of acceptability, is no longer necessary and why a risk-based approach should be universally adopted.

Microorganism lethality requirements for process validation must always be balanced with the need to protect product integrity and patient safety.
Delamination of glass packaging is a source of particulates in parenteral drugs, but identifying the root cause allowed the design of an improved manufacturing process for glass vials.
An integrated approach can improve the efficiency of cleaning validation studies.

A study of root cause in stability samples suggests the need for tighter control of the sodium lauryl sulfate manufacturing processes.
Delivery systems that allow drugs to be administered as liquids, but to form gel within the eye, promise to improve efficacy and patient compliance.
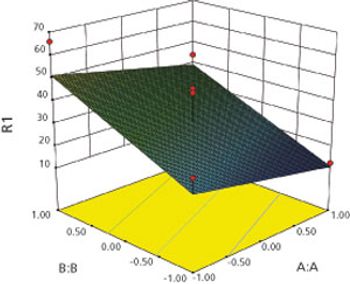
Box-Behnken modeling was used to optimize a resinate complex, to mask the taste of levocetirizine dihydrochloride and montelukast sodium in orally disintegrating tablets.
The author reports results of evaluations and concludes that a disinfectant composed of a low-concentration suspension of silver ions is completely sporicidal with only a one-minute contact time.
The Human Microbiome Project has increased our understanding of the relationship between humans and microorganisms. The authors offer a new perspective on how this knowledge should be considered in setting standards for pharmaceutical quality control in microbiology.

The pharmaceutical manufacturing platforms of fluid-bed granulation and milling are widely used to modify particle size. However, the adoption of process analytical technology to monitor and control these processes is difficult because of their dynamic nature. This study examines the efficacy of a particle characterizing technology to capture particle images under dynamic conditions and to calculate particle size distribution data both in-line and at-line during fluid-bed granulation and milling.
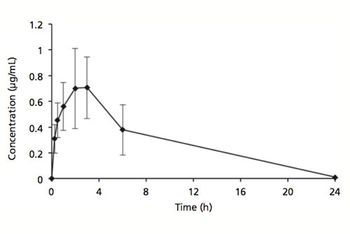
Formulating an injectable solution containing both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs is a challenge.
Tocophersolan or TPGS was developed 60 years ago as a water-soluble form of vitamin E. The author gives an overview of TPGS, including its interesting properties, examples found in the literature, and a brief summary of the regulatory status and marketed formulations.
In anticipation of this mandatory switch from Oxyfume 2000 to 100% EtO for BI testing, comparison studies were performed to determine if the switch from Oxyfume 2000 to 100% EtO would have any impact on BI resistance label claims.
This review highlights relevant physicochemical drug properties and formulation design considerations critical to quality and performance of the sublingual tablets.
Review challenges in the use of normality testing situations and recommendations on how to assess data distributions in the pharmaceutical development manufacturing environment
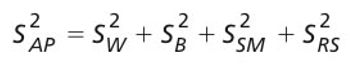
A risk-based guard band surrounds a specification limit and is derived from the uncertainty of the reportable value of the analytical procedure, which includes the uncertainty in the reference standard. The author discusses requirements for generating a reportable value and calculating the associated measurement uncertainty.
Febuxostat is a novel, non-purine, selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase for hyperuricemia in patients with gout. It is the first promising substitute for allopurinol in 40 years. Various synthetic routes to febuxostat, as well as polymorphic forms and impurities of the drug, are reported in the literature. The authors have also identified several impurities that result from the synthesis of febuxostat. This article describes the identification and control of all isomeric, carryover, and byproduct impurities of febuxostat and its intermediates.

A techno-economic profiling method supports pharmaceutical process development by helping identify the best manufacturing approach.
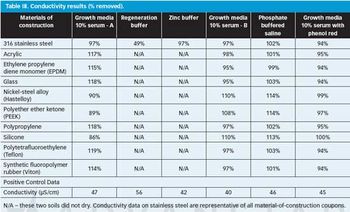
The authors look at the cleanability of pharmaceutical soils from a variety of materials of construction to determine the relative ease of cleaning and explore potential grouping strategies as part of a comprehensive cleaning validation program.

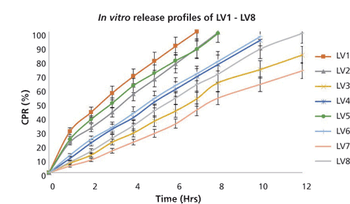
Zero-order release of a freely water-soluble active drug can be obtained using release-controlling polymers.

A new process analytical technology based on impedance spectroscopy has potential applications for characterizing product attributes during the freeze-drying process.

The extended-release performance of drug-loaded pellets manufactured by two methods, drug layering and direct pelletization, was compared.
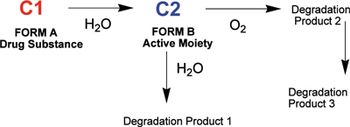
In this article, the authors demonstrate that a normal-phase chromatographic method was stability-indicating for a water-sensitive prodrug. The stress conditions using aqueous and non-aqueous conditions were also compared to understand the information obtained with each approach.
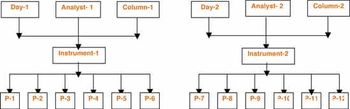
The authors describe the development of a stability-indicating reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic (RP?HPLC) method for the quantitative determination of potential genotoxic impurities present in pemetrexed disodium (form-IV). The chromatographic separation was achieved on a RP?HPLC column (Zorbax SB-Phenyl, Agilent) at ambient temperature with gradient elution using mobile phase A (trifluoroacetic acid [TFA] in water) and mobile phase B (TFA in acetonitrile).

Different approaches for qualification of personnel for visual inspection of residues on equipment surfaces are reviewed.
The industry lacks an accepted method for establishing a minimum incubation time (MIT) of less than seven days for biological indicators (BIs). The authors propose an MIT method that provides a means for reproducible determination of BI grow-out time.