
US Pharmacopeia apparatuses for testing the dissolution of transdermal drugs produce good, reproducible results. Yet some scientists believe that further modifications could improve the instruments? suitability for this application.

US Pharmacopeia apparatuses for testing the dissolution of transdermal drugs produce good, reproducible results. Yet some scientists believe that further modifications could improve the instruments? suitability for this application.

Life-sciences companies spend proportionally more resources on information technology and get less in return on their investment than companies in other industries. The poor return on investment partly results from regulatory costs that are unique to the pharmaceutical industry, but also stems from a failure to manage data strategically.

PharmTech's monthly newsletter, Equipment and Processing Report, reviews the Editor's Picks for the May 2010 edition from ATMI and SciLog.

The author proposes techniques, based on Six Sigma methods, for monitoring such processes to discover their airflow patterns and reduce opportunities for spillage.This article is part of PharmTech's supplement "Solid Dosage and Excipients 2010."

The authors describe the origins of single-use components and explain their application to aseptic processes. They also show how disposable devices have changed over time and offer a glimpse of the future.

Drugmakers have many incentives to avoid overfilling their containers, including the scarcity, and correspondingly high cost, of certain cells and ingredients. These concerns highlight the need for techniques that can fill small volumes of product with great accuracy. Many strategies are available to the industry, but which one works best?

Leading experts share insight on the current and future direction of process analytical technology. This article contains bonus online material.

Endotoxin removal from a finished product is a major challenge for biopharmaceutical manufacturers; particularly as all endotoxin removal methods have operational limitations and may result in loss of protein.

Drugmakers have the common goal of manufacturing safe and sterile pharmaceutical products and understand that the filtration process is a critical means of achieving this goal. Preuse filter-integrity testing provides evidence that a filter will perform correctly, has the right pore size, and has been installed correctly.

A look at the true cost-drivers of cell-culture production.
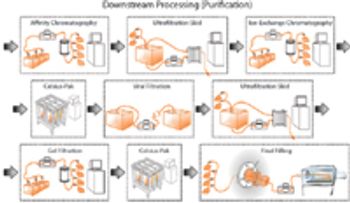
The authors discuss current and future disposable technologies and outline the validation and qualification steps that would be required for a possible disposable process stream.

The authors review the role of automation in aseptic processing and describe their experience in implementing advanced technologies, including the use of isolators and robotics.

The spotlight on the biopharmaceutical industry is intensifying, as recently evidenced by Pfizer's (New York) ongoing acquisition of Wyeth (Madison, NJ), which was initiated partly to reduce the former's dependence on small-molecule drugs.
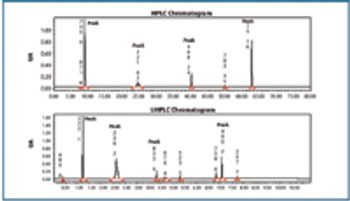
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography is advantageous in a contract laboratory because it is faster, more sensitive, and relies on smaller volumes of organic solvents than HPLC.

A book about pharmaceutical analysis engages the reader with history and unexpected asides.

A well-balanced guide to industrial bioseparations provides valuable information.
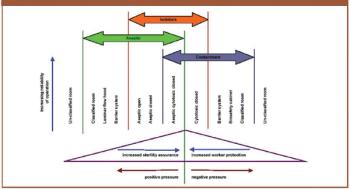
The author discusses the key issues to consider when using isolators such as containment, protection of personnel, the efficiency of biodecontamination cycles, sterility assurance levels, barriers and their integrity, and environmental impact.

Brief pharmaceutical news items for June 2008.

In this topical review, the authors discuss the rationale behind microstructural requirements for biopharmaceutical equipment and problems that may be encountered during the fabrication of high-performance corrosion-resistant equipment.
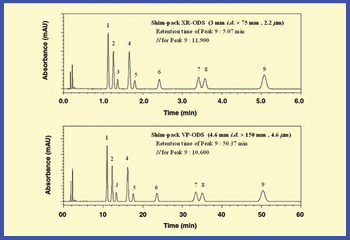
The authors review methods for reducing analysis time and increasing throughput that are reliable and maintain data integrity.
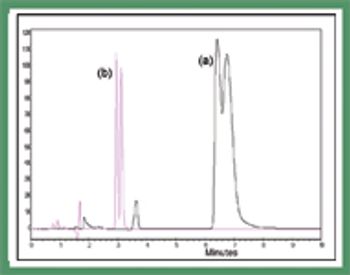
Polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases have been developed that comprise chiral selectors immobilized on their support rather than being physically coated. These materials are completely solvent stable, thereby increasing selectivity and and enabling the development of new chiral selectors that have been too unstable in a coated form for general use.

The combination of supercritical fluid chromatography with chiral separation media offers several analytival advantages over traditional liquid chromatography techniques.
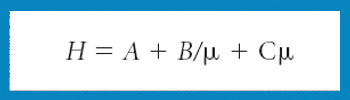
Ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography maximizes efficiency, but, as defined by the resolution equation, the stationary phase is still a crucial consideration when attempting to resolve mixtures of compounds.

High performance liquid chromatography has become an efficient technique at the production scale, and simulated moving bed chromatography provides several benefits during processing.
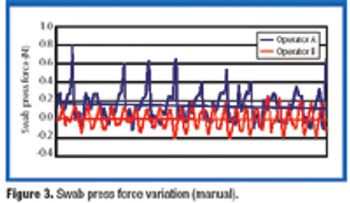
This article presents a study of an aseptic environmental monitoring system for surface contamination at critical areas using a robot.