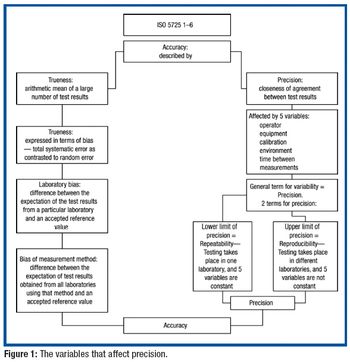
USP applies metrological principles to the dissolution procedure alone and in collaborative studies to understand and minimize potential sources of variability.


USP applies metrological principles to the dissolution procedure alone and in collaborative studies to understand and minimize potential sources of variability.

There is a tremendous need to enhance delivery of potential therapeutics to the brain for treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders. The blood brain barrier (BBB) restricts and controls the exchange of compounds between the CNS and the blood, which requires discovery of new modalities allowing for effective drug delivery to the CNS. Polymer nanotechnology has now become one of the most attractive areas of pharmaceutical research. This review focuses on the current progress in polymeric nanoparticles, where the specific arrangement of the polymeric matter at the nanoscale is utilized to design drug delivery systems that provide safe and efficient transport of CNS drugs across the BBB.

One of the major concerns with introducing PAT, however, is that the bias towards process engineering may not ultimately lead to complete control of product quality.
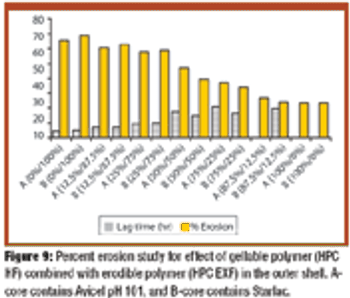
The authors prepared and tested press-coated tablets with various weight ratios of ethylcellulose to hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) and various ratios of two different batches of HPC as an outer coating shell and fillers in core tablets. The tablets were examined for changes in time lag and release patterns of salbutamol sulfate.
Hydrogels are biocompatible drug delivery systems by which the physical properties can be controlled by the cross-linking density. Hydrogels were prepared by copolymerization of acrylic acid monomers in the presence of poly(ethylene glycol)(PEG) to form polyethylene diacrylate (PEDGA). Various molecular weights of PEGs were used for the synthesis of PEGDA to study the effect of molecular weight of PEG on the properties of hydrogels. These hydrogels were further characterized for free water, swelling behavior, water diffusion, drug loading, and drug release profile. By analyzing the swelling behavior and release pattern of the hydrogels, the authors show that these systems can be suitably used for controlled delivery of drugs.
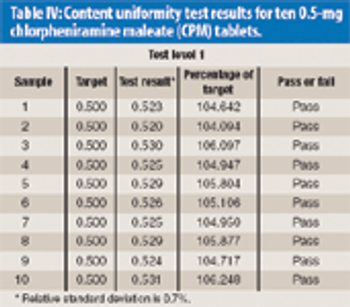
Near-infrared (NIR) assay and content uniformity of tablets provide fast, accurate means of monitoring tablet production that are in step with FDA's process analytical technology initiative.The authors discuss the process for testing a newly released NIR tablet analyzer to determine instrument precision and accuracy using chlorpheniramine maleate tablets.The data show promising results that could relieve laboratory workload of high-performance liquid chromatography analysis and bring analysis closer to real time for process monitoring.

A wealth of citations helps illustrate the applicability of the analytical methods and also highlights their pitfalls.
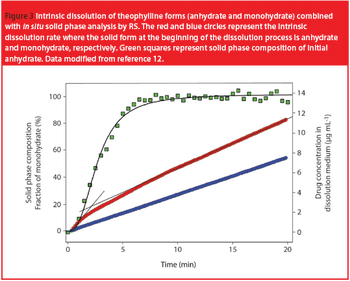
When a dosage form or an API is introduced to the gastrointestinal tract, or dissolution media mimicking it, a transformation from a metastable to a more stable form with lower solubility and bioavailability is possible.

Just because the wheels are turning doesn't mean they're going forward.
The objectives of this study were to prepare and characterize inclusion complexes of lovastatin with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβ-CD) and to study the effect of the complexes on the dissolution rate of lovastatin (LVS). The findings suggest that LVS's poor dissolution profile can be overcome by preparing its inclusion complex with HPβ-CD.
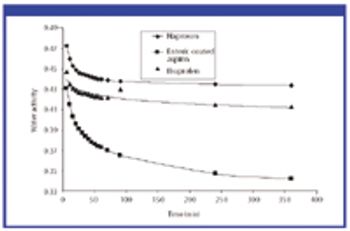
For solid oral-dosage forms, water testing usually is performed to control the chemical, physical, or microbiological properties of the drug product. Measurements of total water as made with Karl Fischer (KF) techniques is not needed and water-activity often will provide a better correlation with changes in chemical, physical, or microbiological properties than KF techniques. In these cases, water activity testing can easily replace KF testing. Water-activity measurements are nondestructive, require little labor, and the equipment required is generally inexpensive. Only a few simple checks are needed to ensure the validity of measurements. Strategies for implementing water activity testing are described.
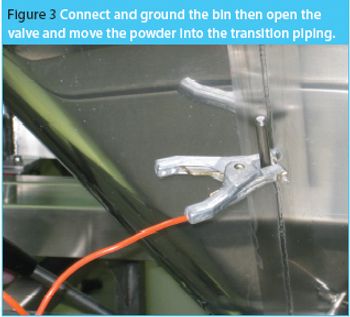
The same phenomena that create lightning and thunderstorms are around us every day, producing incredibly high voltages, which cause sparks and shocks. Static electricity is a mighty force. Each year excessive electrical charge build cause explosions in the grain industry.1 Look around any flammable storage area and you will see both grounding bars on the wall and cables, from the grounding bars connected to the drums of solvents. Take any material safety data sheet (MSDS) for a powder and look in section V; it highlights that any dry powder has the potential to attract and store a charge.

Pfizer's restructuring plan provides yet another example of new supply-chain strategies by the pharmaceutical majors, which involve rationalization of manufacturing facilities and cost improvement. A review of these moves, an outlook for the pharmaceutical market in 2007, and analysis of US pharmaceutical production and trade.
Water interacts with pharmaceutical solids at virtually all stages of manufacture, from synthesis of raw materials to the storage of the final dosage form. The interactions of water with powders is, therefore, a major factor in the formulation, processing and product performance of solid pharmaceutical dosage forms.
This article describes the design and development of a material-sparing fluidization segregation tester for use with pharmaceutical powders. This tester offers several improvements over the current ASTM standardized test practice. Less than 20 mL of material is required to characterize the fluidization segregation potential of a sample. Features of the tester include powder containment for potent compounds, in-process monitoring of the fluidization conditions, and sample retrieval without the need for subsampling or riffling for typical analyses.

AAPS, San Antonio (Oct. 31)-As biologic-based drugs become an increasingly larger part of pharmaceutical product portfolios, strategies for optimizing their formulation become increasingly important.

AAPS, San Antonio (Oct. 30)-Aiming to provide a greater understanding of coating processes, speakers at the 20th Annual Meeting of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists presented some of the difficulties, tools, and strategies for obtaining adequately uniform films in pan and fluid-bed coating processes.

San Antonio, TX (Nov. 1)-Though the US Food and Drug Administration's final guidance on process analytical technology (PAT) was published in Sept. 2004, companies are still unsure about how exactly to implement PAT in their processes.
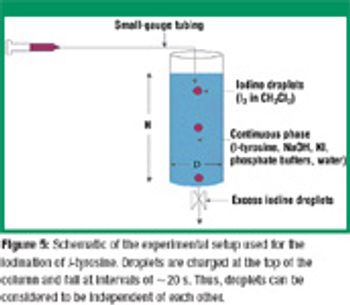
Understanding the impact of reactive mass transfer and local flow in multiphase systems is crucial for maximizing reaction selectivity and minimizing the formation of byproducts. The authors study the influence of mixing on fast liquid–liquid reactions. The iodination of L-tyrosine was used to demonstrate the relationship of droplet size and shape on reaction selectivity and to verify computational predictions. By understanding that droplet dynamics affect the yield and selectivity of fast reactions, the formation of byproducts can be minimized by optimizing operating parameters.
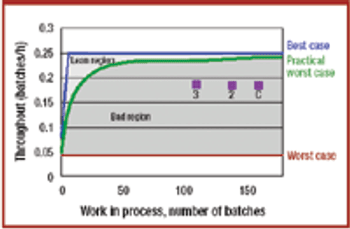
Pharmaceutical companies are facing increased competition, cost pressures, and a need to improve the performance of their manufacturing operations. Lean manufacturing offers methods, tools, and heuristics for improved efficiency in manufacturing. Process analytical technology offers alternative analysis techniques that could greatly improve manufacturing quality and efficiency. Mathematical tools exist for assessing the efficiency of manufacturing processes. Internal benchmarking is recommended for determining the efficiency and tracking improvements in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
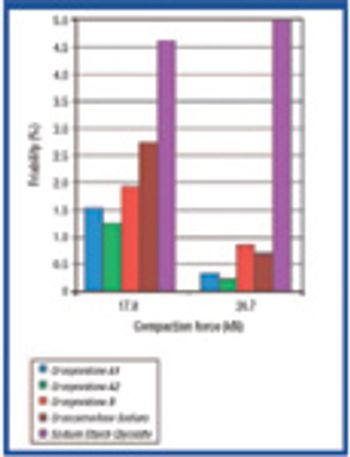
The increasing popularity of orally disintegrating tablets has led to growing interest in the advantages of superdisintegrants. This article presents some practical considerations in selecting these ingredients.

As the pace of product development accelerates, the approach to dissolution-method development must advance beyond a manual method and an assay. A natural progression of the method-development process must include the transfer of the manual method onto automated instrumentation.

West Point, PA (Jul. 31)?A survey of 150 US pharmacists found that nearly 80% believe that "multiple look-alike medications" make it difficult for consumers to identify the correct medication, especially when the drugs are moved to unlabeled containers.

Aegis Therapeutics (San Diego, CA) has launched a new formulation technology to increase the stability of proteins and peptides.

Roxane Laboratories (Columbus, OH), a Boehringer Ingelheim company, is conducting a voluntary recall in the United States and Puerto Rico of a single manufacturing lot of "Azathioprine"tablets, USP 50 mg.