
pharmaceutical science and technology news

pharmaceutical science and technology news

Added functionality excipients facilitate the development of novel drug delivery methods and improve processing techniques.

Currently, high-production rates and continuous production processes favor existing tableting technologies. However, if tablet development becomes rate-limiting in the future, alternative technologies may prove attractive.

Some of the common problems faced by formulators and how using ion exchange resins may be able to solve them are discussed.

Recent advances in spray-drying technology have led to the production of new directly compressible lactose grades with distinct advantages.

Recent technology improvements have made acrylics the preferred system for the aqueous enteric coating of tablets.
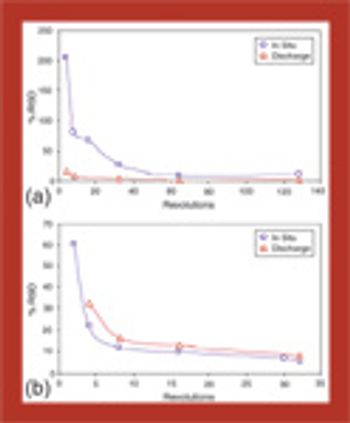
In this series of articles, bin blender performance is comprehensively reviewed using both free-flowing and cohesive mixtures. In part 1, an introduction to tools and techniques is presented, followed by an examination of parameter effects, mixing mechanisms, and the effects of cohesion on mixing.

The author describes a separation method for two active ingredients in the contraceptive pill with liquid chromatography UV detection.

The author suggests that an excipient's functionality can only be determined in the context of a specific formulation and manufacturing process.

Pharmaceutical science and technology innovations

Bin blender performance is comprehensively reviewed using both free-flowing and cohesive mixtures.

Dry powder inhalers are a well-accepted dosage form for pulmonary drug delivery and a wide variety are either currently available or in development. This article examines a premetered, capsule-based multidose inhaler for which different qualities of a-lactose monohydrate were screened.

The bioavailability of some insoluble drugs is enhanced when they are dissolved in the solubilizing agent macrogol 400, although conventional hard capsules cannot tolerate the agent. This article investigates a PVA copolymer, which has been developed by the authors, examining its properties and its suitability as a material in capsule formulations.

This article describes the use of a one-pot processor for the cleaning and cleaning validation of two drug compounds - water-soluble theophylline and water-insoluble mebendazole. Both substances were produced using wet granulation and microwave drying, after which the processor was cleaned using its clean-in-place (CIP) system. Swab samples were taken from areas considered critical during processing and analysed for remains of active ingredient. It was concluded from the results that the processor's CIP system is capable of removing both moieties to a level well within accepted regulations.

The authors examine the development and performance of coprocessed excipients, including testing them for flowability, compressibility, amd dilution potential.

This article reflects on the challenges that predicting powder flowability currently pose to the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry and considers some of the benefits that can accrue when companies overcome these issues.

The use of solid dispersion technology to increase the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs has always been limited by processing and scale-up difficulties. A new approach may help to overcome some of the problems.

The aim of this study was to validate the automated clean-in-place (CIP) system installed on a capsule filling machine to determine its ability to adequately eliminate contaminants. The results obtained from the proposed cleaning validation trial showed that all the soluble tracer was removed after the washing procedure. At the end of the CIP procedure, the discharged water had the same pH, phosphate content and total organic content as the supplied water. Lack of cross-contamination in the product was also demonstrated and a recovery trial highlighted the complete elimination of the tracer from the machine.

This article describes a method for assessing the similarity of dissolution profiles using Hotelling's T2 statistic. The method applies a covariance structure that accounts for the heterogeneity of variance and correlation across time points. Comparing the method with the f2 criterion recommended in FDA's guidance on dissolution testing, the performance of the two methods was assessed on real examples, and simulation studies were also done to compare the method's performance with that of the f2 criterion.
Modern tablet production facilities are faced with two increasingly important, yet contradictory, demands - being able to handle more potent drugs and, at the same time, reduce costs. Additionally, batch sizes must become smaller and production planning more flexible. Until recently, these issues could only be dealt with individually and not as a whole; however, the exchangeable functional module (EFM) may provide a solution to this problem, as this article describes.

The authors provide a combined source of density data and show that denity can be used as an equipment-independent sclaing parameter in the manufacture of common pharmaceutical solids.

Oral dosage forms are the most popular way of taking medication, despite having some disadvantages compared with other methods. One such disadvantage is the risk of slow absorption of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), which can be overcome by administering the drug in liquid form and, therefore, possibly allowing the use of a lower dosage.

Binder properties of mucilage of starches extracted from breadfruit and cocoyam were investigated in paracetamol tablet formulations using tablet physical properties, disintegration times, and dissolution rates as assessment parameters.

The tabletting properties of a new coprocessed excipient for direct compression were compared with a physical mixture of its components (separately and with drugs) and the individual constituents. The compaction properties were also investigated. Results indicated that the new excipient has excellent flow properties and demonstrates enhanced compressibility.
Medicines and excipients are inseparable, with few exceptions - one cannot exist without the other. The Pharmaceutical Quality Group and other international bodies have developed good manufacturing practice (GMP) standards and guidelines to facilitate the effective supply of excipients. This article discusses the definition and significance of excipients, and highlights the importance of implementing the correct excipient manufacturing controls and standards.