
The authors study the effects of sweet potato and cocoyam starches on the compressional and mechanical characteristics of a paracetamol tablet formulation using cornstarch BP.


The authors study the effects of sweet potato and cocoyam starches on the compressional and mechanical characteristics of a paracetamol tablet formulation using cornstarch BP.
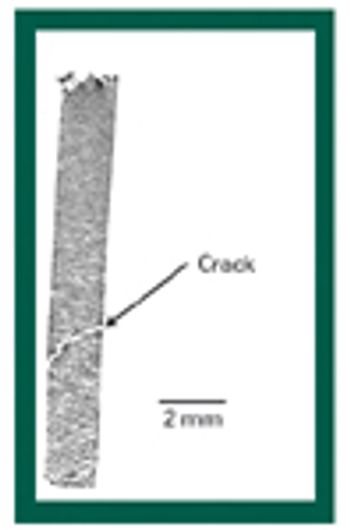
X-ray microtomography has great potential for improving the understanding of the structural features of solid dosage forms and the changes in those features during manufacturing, handling, and storage. This article describes the basic principles of the technique and provides examples of its potential applications.

Big Pharma Companies Team Up to Develop Once-Daily, Triple-Combination HIV Drug

New fixed-dose combination drugs aim to enhance safety and efficacy, while regulators clear a path for more drug–device combination products.

The author points out some major obstacles to effective scale-up and describes methods available to pharmaceutical scientists for addressing scalability issues.

In the manufacture of many pharmaceutical products, dry-particle blending is a critical step that directly affects content uniformity.

Extrusion-spheronization and pellet compression are effective means of developing first-order kinetic, controlled-release drug delivery systems of azithromycin (AZI). The authors prepared, evaluated, and optimized AZI formulations and assessed the stability of the selected formulation under accelerated storage conditions.

Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Innovations

Laser-Marking Technique Improves Tablet Branding

Albumin-Bound Nanoparticle Drug Nabs FDA Approval

The author reviews the effects of moisture on flow properties, tensile strength, Heckel plot, energies involved in compaction, and elastic recovery.

From solving complex formulation challenges to delivering full product-development programs, outsourcing services organizations provide valuable expertise, experience, and technical know-how.

The authors examine the effects of three superdisintegrants on the dissolution and absorption of tenoxicam from solid-dispersion formulations.

Microspheres of Eudragit RL were developed for colonic delivery of albendazole. The effects of polymer concentration, stirring rate, and concentration of emulsifier on particle size and drug loading were studied. A comparative in vitro drug release study of the optimized formulation was carried out.

Size reduction of materials through comminution is employed in many industries, including agrochemicals, minerals, ceramics and pharmaceuticals. The reasons for particle size reduction depend on the industry in question. Within the pharmaceutical industry, a large percentage of products are formed from powders and undergo processing to improve dosage form properties. Particle size reduction prior to compacting to tablets can aid with dissolution and homogeneity. Such processing of powders is, in part, dependent on their mechanical properties and balancing these properties is crucial in achieving desired manufacturing performance. Generally, pilot-scale milling trials are run to determine the most effective and efficient mill and operating conditions for each material. These trials, however, require relatively large quantities of material as well as time, and are normally run in early development when sufficient material becomes available. Hence, it would be highly beneficial to identify a physical property..

With creative engineering and sophisticated chemistry, industry scientists offer big solutions for attaining small particle sizes and narrow distributions.

Freeze pelletization is a new and simple technique for producing spherical pellets for pharmaceutical use.

Using dimensionless analytical models, the authors establish the relationships among the essential parameters of a kneading complexation process.


The authors suggest a design strategy for an aseptic process simulation that focuses on the basic repeating unit of the process, establishing alert and action criteria for the unit itself, and using worst-case simulations to establish routine operational parameters for the manufacturing process.

A straightforward approach reveals how the probability of passing the USP content uniformity test can be calculated for tablets and capsules.

In this final part of a series of three articles, the results from experiments involving cohesive materials are discussed in terms of mixing performance, agglomerate comminution, and lubrication of powder mixtures.
This article reviews various physicochemical approaches that may be employed to enhance absorption following oral administration of solid dosage forms in humans. This article also examines strategies based on capitalizing or neutralizing physiological processes.

A novel probe design can reduce the powder-sample density variance such that moisture and solvent levels can be accurately modeled and predicted in process.

The results of forced degradation studies indicate the need for alternatives to valerophenone as an internal standard calibration for quantifying ibuprofen in bulk drug and tablet assay samples.