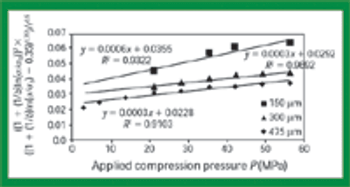
Quantitative data from the literature show strong relationships among average particle size, powder densification, tensile strength, and hardness.

Quantitative data from the literature show strong relationships among average particle size, powder densification, tensile strength, and hardness.
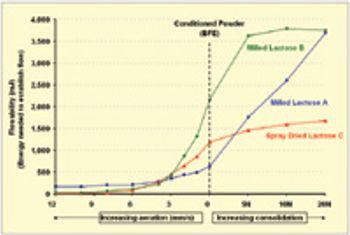
The pharmaceutical industry's focus on process understanding, monitoring, and control is driving manufacturers to take greater steps toward identifying possible manufacturing bottlenecks earlier in the development process. For tablet, capsule, and excipient producers, such efforts include taking a closer look at the flow-ability of their powders.
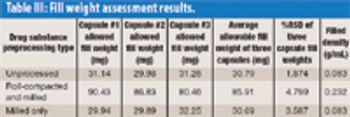
Using a novel automated microfilling system, the authors demonstrate that roller compaction followed by milling is a viable preprocessing technique for high-dose chemical-in-capsule dosage forms. The process results in higher bulk and tapped densities for drug substances compared with milling alone.

Though dissolution testing has been under scrutiny, it is still a powerful test method.
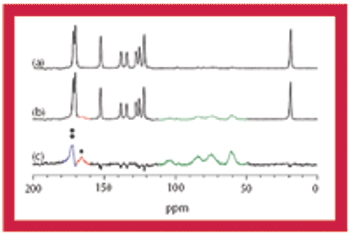
This article discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using solid-state NMR spectroscopy for the analysis of pharmaceutical solids.
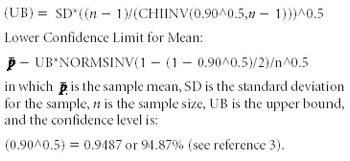
Using the Bergum Method and the MS Excel software program, the author determines the probability of passing the USP dissolution test.
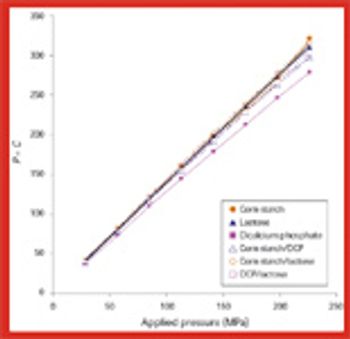
The survival of Bacillus subtilis spores in dicalcium phosphate, lactose, and corn starch and in their binary mixtures depends on the compressional properties of these materials and on parameters involved during the tableting process, including compression speed.
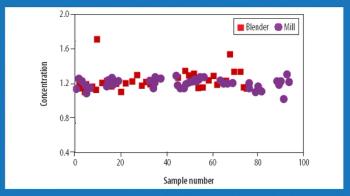
Almost all pharmaceutical manufacturing processes require handling and processing cohesive powders. The application of sufficient shear (i.e., the total deformation that the bulk of granular material undergoes under applied shear stress) is an essential factor in such processes. Sufficient shear is required to mill and de-lump materials, achieve sufficient flow, and homogenize cohesive ingredients. Shear mixing plays a critical role in the blending of dry powders, particularly for those that contain a minor cohesive component such as a solid lubricant or a drug. This mechanism is necessary to achieve a satisfactory homogeneity and disintegrate possible agglomerates. Excessive shear can be disadvantageous, however, and can lead to electrostatic buildup, attrition, and overlubrication.
Solid oral drug products are one of the oldest of all manufactured dosage forms (1). Today, the development of an appropriate formulation of drug and excipients and of an effective manufacturing process to create a tablet or capsule is slowly transforming from a practice of applied art to one of applied science. The US Food and Drug Administration supports this change by expecting sponsors of new drug applications to understand, describe, and control materials and processes as well as the risks associated with drug product manufacturing (2). These steps will ensure the consistent production of products that meet their specifications and remain safe and effective during their shelf life.

Control Development's (South Bend, IN, www.controldevelopment.com) blend uniformity and dryer monitor consists of a NIR spectrometer, a sampling head, computer, and software.

Generally, tablet and capsule film coatings are applied as aqueous or organic-based polymer solutions or dispersions, graduate student Sagarika Bose (University of Connecticut) explained during her Tuesday AAPS Graduate Student Symposium presentation, "Development and Evaluation of Solventless Photocurable Pharmaceutical Film Coating." However, organic film coatings can be flammable, toxic, and must comply with strict environmental regulations. Aqueous film coating can lead to the degradation of certain drugs by heat and water.
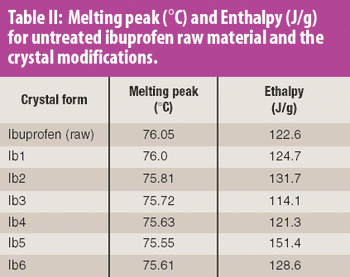
The common crystal form of ibuprofen was changed to optimize processing and manufacturing properties. Six modified crystal forms were prepared and assessed for dissolution, morphology, particle size, density, thermal characteristics, powder x-ray diffractometry, flow properties, and tabletability.
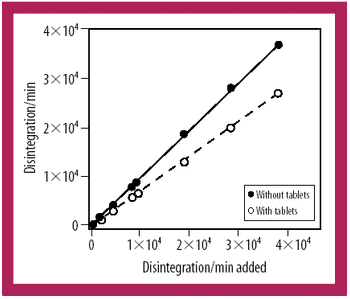
A radiotracer technique is a simple, fast, and sensitive technique for analyzing the integrity of clinical supply packages to water.

This review article discusses orally disintegrating tablets and their manufacturing technologies, development issues, and future trends.
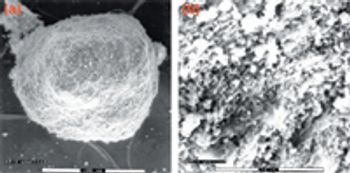
Although agitation improves drying efficiency and ensures uniformity of the final dry material, it can also affect the physical properties of the product as it dries. This study evaluates the effect of scale up and equipment selection on an active ingredient undergoing granulation during the drying process.

Pharmaceutical science and technology innovation

The tablet formation of six different carrageenans was analysed by 3D modelling, Heckel analysis, the pressure–time function and energy calculations. It was found that the fibres experienced plastic deformation, which was accompanied by a great deal of elasticity. Measurement of elastic recovery in dependence on maximum relative density and time showed that relaxation is completed a considerable amount of time after tabletting. Shrinking of the fibres occurred in parallel with elastic recovery as a result of the reorganization of the fibre structure. The tabletting behaviour of carrageenans makes them suitable for the soft tabletting of pressure sensitive materials.
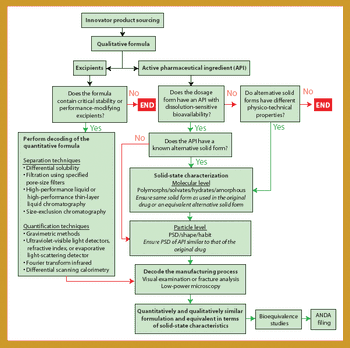
Being the first to gain the most is a fundamental principle in the generics business because several companies compete to create generics of successful products going off patent. For a generics company to maintain revenue growth in a market in which product prices continue to fall, it must secure a continuous flow of new products, with quality and speed to market being key drivers. Thus, generics companies must be highly skilled in product and process development (1), the generics business, and achieving bioequivalence-the most critical development area.
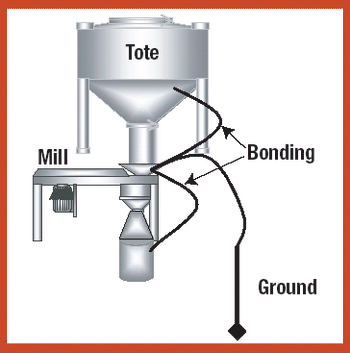
Various systems and measures can be used to safely handle and process explosive pharmaceutical compounds in a range of manufacturing procedures.

The aim of this study was to analyse the process of tablet formation and the properties of the final tablets for six different carrageenans. The carrageenans used were based on the basic types of ?-, ?- and ?-carrageenan. Microcrystalline cellulose was used for comparison. Determination of material properties, compression analysis and tablet properties were described. Water content, particle size and morphology, glass transition temperature, and crystallinity were studied. The results show that the carrageenans are predominantly amorphous fibres, which are in the rubbery state during tabletting.

Able Labs Files for Chapter 11

Chiron Cuts Supply of Flu Vaccines Made in Germany; Liverpool Plant Under Inspection

Able Interim Chief Resigns Amid Drug Recall

A stepwise, process risk-assessment approach can facilitate the identification and understanding of critical process parameters, quality attributes, and in-process controls. This approach can lead to more use of science- and risk-based regulatory practices to simplify the regulatory requirements for changes to synthetic processes and to support the underlying quality systems that ensure compliance.

Self-Assembly Nanotechnology Improves Microencapsulation