
The Impurity Profiling Group reviews stress testing according to regulatory guidance documents. The authors emphasize what should be considered for late clinical phases and for registration application dossiers.
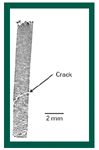

The Impurity Profiling Group reviews stress testing according to regulatory guidance documents. The authors emphasize what should be considered for late clinical phases and for registration application dossiers.

Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Innovations

Analytical instrument suppliers are developing manufacturing-tailored tools that are small, precise, and easy to use.

The United States Pharmacopeia should not change its philosophical position on singlet testing.

A swab-sampling method was developed for cleaning validation of a residual active pharmaceutical ingredient in samples collected after cleaning the sampling suite. A summary of the strategies and results of the method development is presented.

Comparative studies of the US Pharmacopeia (645) "Conductivity" and the European Pharmacopeia "Heavy Metals" tests were conducted to demonstrate that the USP method can determine the presence or absence of heavy metals in process water samples.

Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Innovations

Laser diffraction is an important technique for particle size analysis. This article highlights the many advantages this tool has to offer.

Pat Survey

This article provides guidance for developing dissolution testing for poorly soluble compounds. It is the second of a series of articles based on material from a 2003 PhRMA workshop about acceptable analytical practices.

Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Innovations

Pharmaceutical Science & Technology News
A harmonized global specification is possible providing that the procedures and acceptance criteria defined are acceptable to regulatory authorities in all regions.

This article provides guidance for minimally acceptable method validation practices and a foundation for assessing the risks and benefits associated with method validation programs.

Pharmaceutical Science & Technology News

By enhancing stability and in vitro drug-release characteristics, limonene enantiomers are a natural-source alternative for developing and characterizing self-nanoemulsified drug delivery systems.

Evaluations have shown, in most cases, visual observations are sensitive enough to verify equipment cleanliness. An experiment was conducted to explore the possibility of using a visible-residue limit as an acceptable cleaning limit in a pharmaceutical research facility, including an evaluation of the limits and subjectivity of ?visually clean? equipment.

Steaming-in-place (SIP) is a widely adopted method for the in-line sterilization of processing equipment. The main advantage of SIP relies on manipulation reduction and aseptic connections that might compromise the integrity of the downstream equipment.
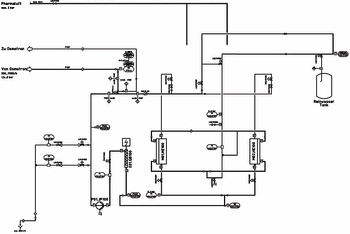
This article describes the quality of highly purified water and its applications, addressing why ultrafiltration (UF) is being used as a downstream purification process. It aims to show that UV is a real alternative for producing pyrogen-free water. This method allows essential cost savings compared with distillation and guarantees a higher safety than other membrane methods such as reverse osmosis.


In the Spotlight-Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Innovations

Emerging high-tech solutions prepare to cater to industrial automation with promises of increased efficiencies, faster communications, and custom applications.

A straightforward approach reveals how the probability of passing the USP content uniformity test can be calculated for tablets and capsules.

The author describes the efforts of the standards committees to establish guidelines for PAT implementation and the impact of the guidelines on the industry.
This article reviews various physicochemical approaches that may be employed to enhance absorption following oral administration of solid dosage forms in humans. This article also examines strategies based on capitalizing or neutralizing physiological processes.