
A Position Paper from the AAPS In Vitro Release and Dissolution Focus Group
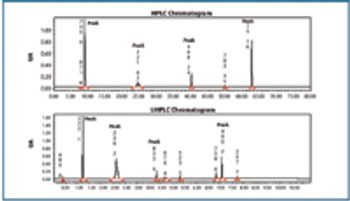
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography is advantageous in a contract laboratory because it is faster, more sensitive, and relies on smaller volumes of organic solvents than HPLC.
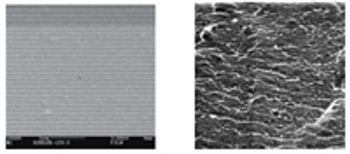
The authors investigate the effects of a polyethylene glycol plasticizer and water on cellulose acetate film properties.
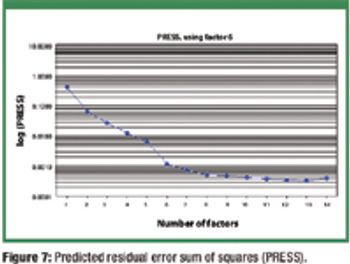
The authors extend the range of a near-infrared calibration model for tablet assay using production 'seed' spectra and synthetic spectra generated from placebos and 'pure' active pharmaceutical ingredient spectra.
The author tests the ruggedness of VRL viewing conditions and defines optimal viewing conditions.
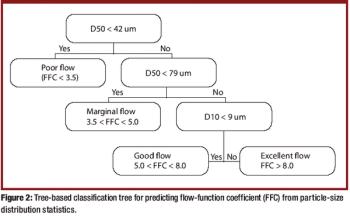
The authors present a simple and material-sparing approach for estimating the powder-flow performance of previously uncharacterized single-component bulk powders when only particle-size distribution data are available.

The authors formulated and developed taste-masked RDFs of cetirizine hydrochloride for patients who experience difficulty in swallowing the tablet dosage form of the drug.

The author defines sanitizers, disinfectants, and antibiotics, and examines the question of whether the rotation of disinfectants is scientifically warranted.
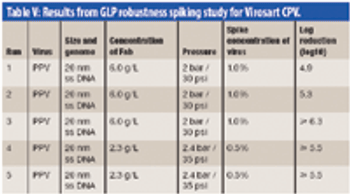
The authors examine the challenges of integrating a large-scale chromatography and nanofiltration process for purification of a polyclonal antibody.

The authors propose that a postapproval management plan can serve as a tool to apply science- and risk-based approaches to the manufacturing process.

The authors propose an approach for qualification-target selection and show how it can be applied to blister-filling and packaging systems.

Hot-melt extrusion offers many advantages compared with conventional solid dosage form manufacturing, and has consequently received considerable attention from both the pharmaceutical industry and academia as a novel drug delivery technology. The possibility of forming solid dispersions with improved bioavailability renders hot-melt extrusion an excellent alternative to other conventionally employed techniques.

The authors evaluated the effect of polymer composition on the drug-release profile and the effect of storage conditions on dissolution characteristics.
The authors review the current regulatory framework for the selection of drug substance starting materials.
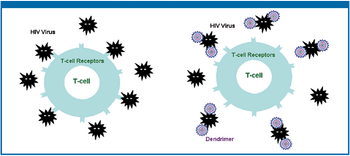
This review provides an update of how dendrimer technology is being applied to the development of novel systems for various topical delivery applications.
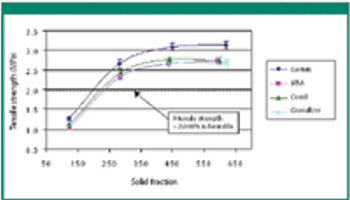
The authors evaluate the effect of various mill types on particle-size distribution, flowability, tabletability, and compactibility.
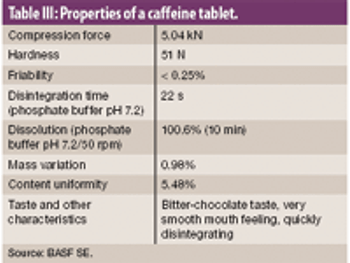
The authors examine the effectiveness of an excipient comprised of mannitol, polyvinyl acetate, and crospovidone using model actives loperamide hydrogen chloride and caffeine.
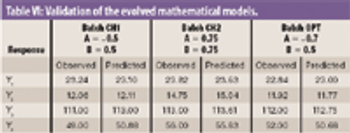
The authors studied the effect of the combination of binders on the flow and compressibility characteristics of the agglomerates of binary combination of lactose and dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate.

This article summarizes the classification systems for topical liquid and semisolid dosage forms used for dermatological application and notes some differences between FDA and USP classification.

Cycle design and robustness testing using advanced process analytical technology.
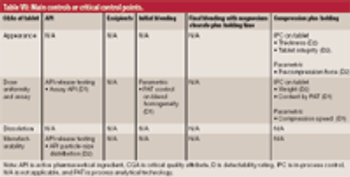
Criticality management combines pharmaceutical product, process, and material knowledge and risk management in one approach, which is reflected in a single document.
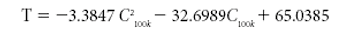
This tutorial paper is meant to aid in dielectric-sensor selection
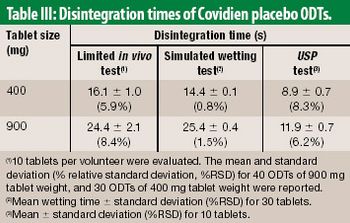
The authors propose an alternative to the USP disintegration test method. The method embraces physiological conditions of the oral cavity, as a screening tool for developing ODT products.

The authors consider several common techniques for verifying the accuracy of liquid-handling equipment and offer guidance for finding the appropriate technique for a given instrument.

The authors describe the factors affecting reconstitution time of dry powder for injection and classifies them as intrinsic and extrinsic parameters.
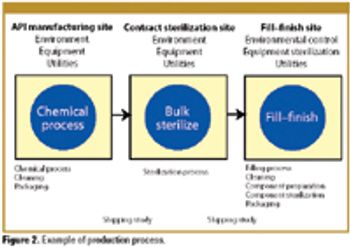
Patient safety must be the primary concern of any validation effort. The author explains how a risk-based approach to validation and compliance follows naturally from this premise.

The author provides an overview of key regulatory issues facing companies seeking to market their biopharmaceutical agents globally.

The authors survey the approved applications of dimethyl sulfoxide USP, PhEur across the healthcare industry and consider the suitability of DMSO from a regulatory and formulation compatibility standpoint.

Enterprise process control and management (EPCAM) is a new strategy for healthcare manufacturers based on recent process-control breakthroughs in the electronics industry.

The US Food and Drug Administration announced its Pharmaceutical GMPs for the 21st Century initiative six years ago. This article reports on the outcome of a recent workshop on this topic and the action plan set forth.