
The authors describe the origins of single-use components and explain their application to aseptic processes. They also show how disposable devices have changed over time and offer a glimpse of the future.

The authors describe the origins of single-use components and explain their application to aseptic processes. They also show how disposable devices have changed over time and offer a glimpse of the future.
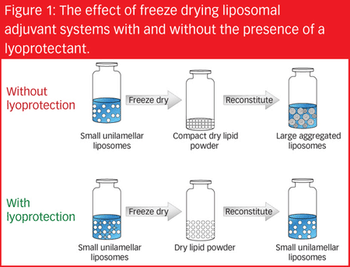
There are a variety of vaccine types, each varying in safety and efficacy, and each possessing its own formulation challenges. To overcome potential instabilities when developing vaccines, one formulation strategy is to produce a dried product.

The most important consideration when choosing a freeze dryer is to ensure the system is fit for both today's applications and future needs.

Pharmaceutical Technology Europe discusses some of the latest challenges and innovations in pharmaceutical lyophilization.

Last year, a member of the PTE editorial team attended the 2nd Annual Lyophilisation Conference in London (UK).

Drugmakers have many incentives to avoid overfilling their containers, including the scarcity, and correspondingly high cost, of certain cells and ingredients. These concerns highlight the need for techniques that can fill small volumes of product with great accuracy. Many strategies are available to the industry, but which one works best?

What have been the key innovations that have shaped current aseptic practices and techniques?

Each sector of the pharma industry is fraught with challenges and weighty regulations; aseptic processes and techniques are no exception.

Closed vial technology has been designed to address the challenges - potential contamination, counterfeiting and process complexity - associated with the aseptic filling of injectable drugs.

The author details the factors in formulation design, requirements in facilites and equipment, and validation criteria for aseptic formualtions.

The author discusses the risks involved with aseptic processing, methods and tools used to identify and control risk, and regulatory guidelines relevant to the risk-management process.

The manufacturing process, which influences a drug's safety and efficacy, is particularly critical for drugs administered through injection, and personnel must closely supervise lyophilization to ensure product quality.
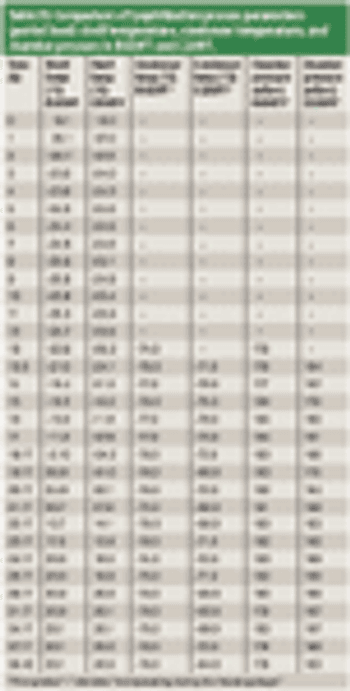
The authors describe a comprehensive methodology for establishing functional equivalence among various lyophilizers.

Why correctly calibrating a drug with its packaging is the key to success.
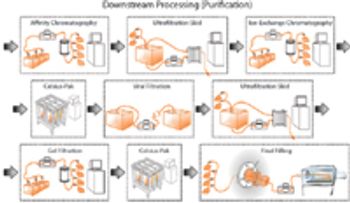
The authors discuss current and future disposable technologies and outline the validation and qualification steps that would be required for a possible disposable process stream.

The authors review the role of automation in aseptic processing and describe their experience in implementing advanced technologies, including the use of isolators and robotics.
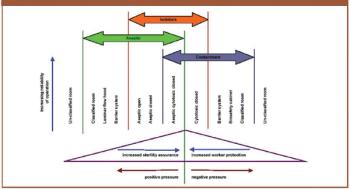
The author discusses the key issues to consider when using isolators such as containment, protection of personnel, the efficiency of biodecontamination cycles, sterility assurance levels, barriers and their integrity, and environmental impact.

A comparison of conventional cleanrooms, restricted access barrier systems, and isolators, shows the benefits of using isolators in high-potency drug manufacturing.

Cycle design and robustness testing using advanced process analytical technology.

The US Food and Drug Administration issued a rule that clarifies its requirements for current good manufacturing practices for aseptic processing, water standards, and verifications standards.
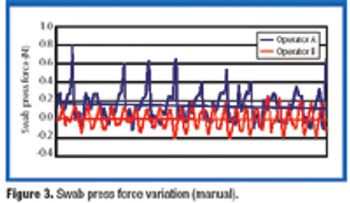
This article presents a study of an aseptic environmental monitoring system for surface contamination at critical areas using a robot.

Irradiation is an established method of sterilization for pharmaceutical products. Radiation sterilization can be achieved with gamma rays, electron beams, and X-rays. Each of these techniques has its advantages and disadvantages. The author describes these methods, the ways to find the correct sterilization doses, and the regulatory and safety concerns about irradation sterilization.

Aseptic processing has advanced over the past several decades, yet the pharmaceutical industry is still accepting of its limitations, particularly as it relates to human intervention as a source of contamination. The authors explain the importance of further diminishing the role of operators in aseptic processing and the approaches and technologies needed to achieve that goal.
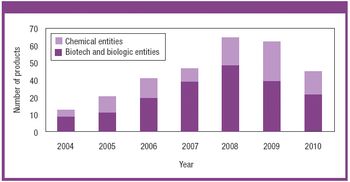
There is a growing need for patient-compliant dosage forms within the cancer therapeutics and biotechnology areas. Ease of administration, enhanced therapeutic efficacy, and reduced side effects are factors that differentiate drug delivery products from conventional dosage forms and provide a competitive advantage. This article reviews salient trends in the parenteral drug delivery sector within the realms of a changing regulatory environment, drivers to growth, and recent advances in this field. Challenges associated with bringing parenteral drug delivery concepts to commercialization are discussed.

This article summarizes changes to the Akers–Agalloco aseptic processing risk analysis model (first presented in Pharmaceutical Technology's November 2005 issue) as well as some of the underlying thinking behind the revision. The simplified model makes the method easier to use because of its greater flexibility of environmental control practice. It maintains the emphasis on human activity as the primary consideration in risk management for aseptic processing.