
Henrik Schwartzbach, senior process technologist at GEA Niro, explins why spray drying is seeing increased uptake in the pharma industry.

Henrik Schwartzbach, senior process technologist at GEA Niro, explins why spray drying is seeing increased uptake in the pharma industry.

The authors question certain aspects of the industry's current regulatory-compliance strategy and suggest that aseptic-process control and evaluation should be revised.

A technical forum moderated by Patricia Van Arnum

We want to fill one of our oxygen-sensitive products inside an isolator system. Can we run an isolator with pure nitrogen and defined humidity?

Regulators question whether particles that they can't see hurt patients.

The authors revisit their previous effort to refine the terms that describe interventions and to dispel confusion that arose after the original article was published.

The application of the first piston syringes to treat medical complications was described in Roman times during the 1st century, and forms of intravenous injection and infusion began as early as 1670.

The growing uptake of single-use sterile packaging in pharmaceutical production processes mirrors the broader trend towards single-use across every sector of the pharmaceutical industry.

A review on the current status of long-acting injectables, including commercially marketed products. This article is part of a special Drug Delivery issue.

The authors describe the origins of single-use components and explain their application to aseptic processes. They also show how disposable devices have changed over time and offer a glimpse of the future.
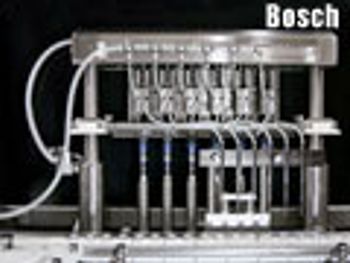
Technological developments make it easier to manufacture sterile parenterals.

Drugmakers have many incentives to avoid overfilling their containers, including the scarcity, and correspondingly high cost, of certain cells and ingredients. These concerns highlight the need for techniques that can fill small volumes of product with great accuracy. Many strategies are available to the industry, but which one works best?

What have been the key innovations that have shaped current aseptic practices and techniques?

Each sector of the pharma industry is fraught with challenges and weighty regulations; aseptic processes and techniques are no exception.

Closed vial technology has been designed to address the challenges - potential contamination, counterfeiting and process complexity - associated with the aseptic filling of injectable drugs.

The author details the factors in formulation design, requirements in facilites and equipment, and validation criteria for aseptic formualtions.

The author discusses the risks involved with aseptic processing, methods and tools used to identify and control risk, and regulatory guidelines relevant to the risk-management process.

Why correctly calibrating a drug with its packaging is the key to success.

To address the increasing popularity of drug-injector systems, the US Food and Drug Administration last week released a Draft Guidance for Industry titled, Technical Considerations for Pen, Jet, and Related Injectors Intended for Use with Drugs and Biological Products.

To address the increasing popularity of drug-injector systems, the US Food and Drug Administration last week released a Draft Guidance for Industry titled, Technical Considerations for Pen, Jet, and Related Injectors Intended for Use with Drugs and Biological Products.
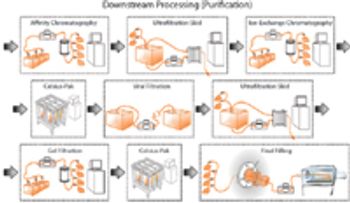
The authors discuss current and future disposable technologies and outline the validation and qualification steps that would be required for a possible disposable process stream.

The authors review the role of automation in aseptic processing and describe their experience in implementing advanced technologies, including the use of isolators and robotics.

Outsourcing sterile manufacturing involves an integrated approach in product life-cycle management.
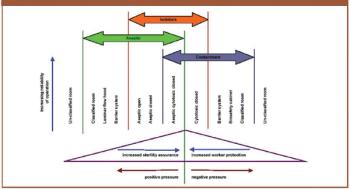
The author discusses the key issues to consider when using isolators such as containment, protection of personnel, the efficiency of biodecontamination cycles, sterility assurance levels, barriers and their integrity, and environmental impact.

A comparison of conventional cleanrooms, restricted access barrier systems, and isolators, shows the benefits of using isolators in high-potency drug manufacturing.